DNA bulges occur when one or more extra bases are added on one side of the DNA strain during the transcription process. These bases generally face either inwards or outwards with respect to the main helix. If we imagine DNA as a straight ladder, a bulge would be a half step that fails to reach the other side. DNA bulges, if not corrected after the transcription process, can often lead to mutations and to the rise of diseases and life threatening conditions. Particular DNA bulges are also relevant in the replication of HIV.
Due to the importance and biological significance of these structures, many studies have been conducted towards the development of molecules that specifically target and recognise these modifications. Molecules have been developed to selectively bind to bulges containing Guanine(G), Adenine(A) and aggregates of Cytosine/Thymine(C/T), but very few show high selectivity for T alone.
Another interesting feature emerging from the study is that when tested on oligonucleotides containing single-base bulges in the stem of a hairpin or a duplex structure, binding occurred without damage to the structure of the stem and only when T was in the bulge. Several other oligonucleotides with different bases in the bulge and with thymine in the hairpin stem (no bulge) were tested to further assess the selectivity of the complex, resulting in only one example of reduced binding when the T bulge has a cytosine on both sides.
NMR titrations were used to follow the binding process thanks to a clear change in the chemical shift of methylenic protons on the base after coordination.
To read the original ChemComm communication, please take a look at:-
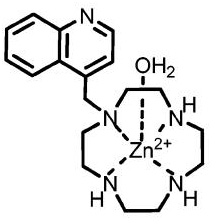
Recognition of thymine in DNA bulges by a Zn(II) macrocyclic complex
Imee Marie A. del Mundo, Matthew A. Fountain and Janet R. Morrow
Chem. Commun., 2011, Advance Article
Posted on behalf of Dr. Giorgio De Faveri, Web Writer for Catalysis Science & Technology.












 Scientists are a step closer to understanding how an important cell organelle works, which could lead to new insight into disease such as diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease.
Scientists are a step closer to understanding how an important cell organelle works, which could lead to new insight into disease such as diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease.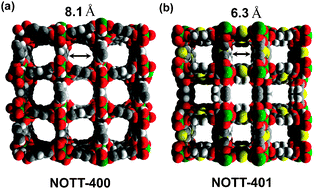 The novel MOFs, NOTT-400 and NOTT-401, share the same metal-based fragment as building block and differ from each other by the organic linker employed (H4BPTC and H2TDA). They retained high crystallinity up to 500 °C and 350 °C respectively and were successfully reacted with acetone and degassed to afford the fully desolvated material ready for use.
The novel MOFs, NOTT-400 and NOTT-401, share the same metal-based fragment as building block and differ from each other by the organic linker employed (H4BPTC and H2TDA). They retained high crystallinity up to 500 °C and 350 °C respectively and were successfully reacted with acetone and degassed to afford the fully desolvated material ready for use.