Have you seen the most-read Chemical Science articles from 2013?
Have you seen the most-read Chemical Science articles from 2013?
Intramolecular C(sp3)–H amination
Jenna L. Jeffrey and Richmond Sarpong
DOI: 10.1039/C3SC51420J
Dialkylbiaryl phosphines in Pd-catalyzed amination: a user’s guide
David S. Surry and Stephen L. Buchwald
DOI: 10.1039/C0SC00331J
The role of organometallic copper(III) complexes in homogeneous catalysis
Alicia Casitas and Xavi Ribas
DOI: 10.1039/C3SC21818J
Design and preparation of new palladium precatalysts for C–C and C–N cross-coupling reactions
Nicholas C. Bruno, Matthew T. Tudge and Stephen L. Buchwald
DOI: 10.1039/C2SC20903A
Chelation-assisted Rh(III)-catalyzed C2-selective oxidative C–H/C–H cross-coupling of indoles/pyrroles with heteroarenes
Xurong Qin, Hu Liu, Dekun Qin, Qian Wu, Jingsong You, Dongbing Zhao, Qiang Guo, Xiaolei Huang and Jingbo Lan
DOI: 10.1039/C3SC22241A
A robust protocol for Pd(II)-catalyzed C-3 arylation of (1H) indazoles and pyrazoles: total synthesis of nigellidine hydrobromide
Mengchun Ye, Andrew J. F. Edmunds, James A. Morris, David Sale, Yejia Zhang and Jin-Quan Yu DOI: 10.1039/C3SC50184A
N-Heterocyclic carbene (NHC)–copper-catalysed transformations of carbon dioxide
Liang Zhang and Zhaomin Hou
DOI: 10.1039/C3SC51070K
Chiral organic contact ion pairs in metal-free catalytic enantioselective oxidative cross-dehydrogenative coupling of tertiary amines to ketones
Gen Zhang, Yunxia Ma, Shoulei Wang, Weidong Kong and Rui Wang
DOI: 10.1039/C3SC50604E
Carbofluorination via a palladium-catalyzed cascade reaction
Marie-Gabrielle Braun, Matthew H. Katcher and Abigail G. Doyle
DOI: 10.1039/C2SC22198E
Pd(II)-catalyzed alkoxylation of unactivated C(sp3)–H and C(sp2)–H bonds using a removable directing group: efficient synthesis of alkyl ethers
Fa-Jie Chen, Sheng Zhao, Fang Hu, Kai Chen, Qi Zhang, Shuo-Qing Zhang and Bing-Feng Shi
DOI: 10.1039/C3SC51993G
Pd-catalyzed oxidative C–H/C–H cross-coupling of pyridines with heteroarenes
Bo Liu, Yumin Huang, Jingbo Lan, Feijie Song and Jingsong You
DOI: 10.1039/C3SC50348H
Catalytic hydrotrifluoromethylation of styrenes and unactivated aliphatic alkenes via an organic photoredox system
Dale J. Wilger, Nathan J. Gesmundo and David A. Nicewicz
DOI: 10.1039/C3SC51209F
Rethinking the term “pi-stacking”
Chelsea R. Martinez and Brent L. Iverson
DOI: 10.1039/C2SC20045G
One-shot indole-to-carbazole π-extension by a Pd–Cu–Ag trimetallic system
Kyohei Ozaki, Hua Zhang, Hideto Ito, Aiwen Lei and Kenichiro Itami
DOI: 10.1039/C3SC51447A
Photoelectrochemical properties of LaTiO2N electrodes prepared by particle transfer for sunlight-driven water splitting
Tsutomu Minegishi, Naoyuki Nishimura, Jun Kubota and Kazunari Domen
DOI: 10.1039/C2SC21845C
Rhodium-catalyzed enantioselective cyclopropanation of electron-deficient alkenes
Hengbin Wang, David M. Guptill, Adrian Varela-Alvarez, Djamaladdin G. Musaev and Huw M. L. Davies
DOI: 10.1039/C3SC50425E
Aminocatalytic remote functionalization strategies
Hao Jiang, Łukasz Albrecht and Karl Anker Jørgensen
DOI: 10.1039/C3SC50405K
Palladium-catalyzed coupling of functionalized primary and secondary amines with aryl and heteroaryl halides: two ligands suffice in most cases
Debabrata Maiti, Brett P. Fors, Jaclyn L. Henderson, Yoshinori Nakamura and Stephen L. Buchwald
DOI: 10.1039/C0SC00330A
On the role of anionic ligands in the site-selectivity of oxidative C–H functionalization reactions of arenes
Italo A. Sanhueza, Anna M. Wagner, Melanie S. Sanford and Franziska Schoenebeck
DOI: 10.1039/C3SC00017F
Copper-mediated trifluoromethylation of propiolic acids: facile synthesis of α-trifluoromethyl ketones
Zhengbiao He, Rui Zhang, Mingyou Hu, Lingchun Li, Chuanfa Ni and Jinbo Hu
DOI: 10.1039/C3SC51613J
Synergistic catalysis: A powerful synthetic strategy for new reaction development
Anna E. Allen and David W. C. MacMillan
DOI: 10.1039/C2SC00907B
Ruthenium-catalyzed ortho-C–H bond alkylation of aromatic amides with α,β-unsaturated ketones via bidentate-chelation assistance
Guy Rouquet and Naoto Chatani
DOI: 10.1039/C3SC50310K
Development of a generic activation mode: nucleophilic α-substitution of ketones via oxy-allyl cations
Mark N. Vander Wal, Andrew K. Dilger and David W. C. MacMillan
DOI: 10.1039/C3SC51266E
Rh(III)-catalyzed C–H activation/cycloaddition of benzamides and methylenecyclopropanes: divergence in ring formation
Sunliang Cui, Yan Zhang and Qifan Wu
DOI: 10.1039/C3SC51424B
Cross coupling of thioethers with aryl boroxines to construct biaryls via Rh catalyzed C–S activation
Fei Pan, Hui Wang, Peng-Xiang Shen, Jing Zhao and Zhang-Jie Shi
DOI: 10.1039/C3SC22242J
Chemical Science is the Royal Society of Chemistry’s flagship journal; publishing research articles of exceptional significance and high-impact reviews from across the chemical sciences. The journal’s latest (2012) Impact Factor is 8.3. Research in Chemical Science is not only of the highest quality but also has excellent visibility; this is reflected in our latest citation profile.
Submit your exceptional research to Chemical Science today!
Stay up to date with Chemical Science
Be among the first to hear about the newest articles being published – Sign-up to our journal news alert to receive information about most read articles, journal news, as well as calls for papers and invitations.














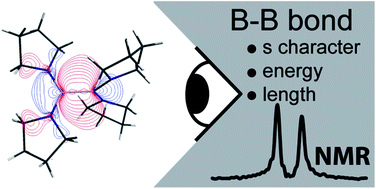
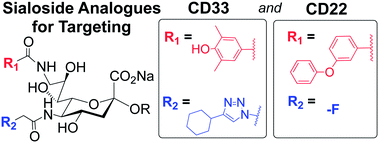

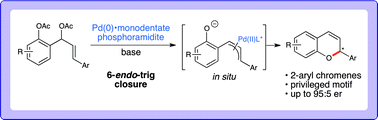

 Have you seen the most-read Chemical Science articles from 2013?
Have you seen the most-read Chemical Science articles from 2013?