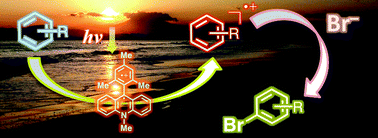
A greener, non-toxic method for brominating aromatic hydrocarbons has been developed by Japanese scientists. Using 9-mesityl-10-methylacridinium ion as the photocatalyst, Shunichi Fukuzumi‘s team at Osaka University selectively brominated a range of aromatic hydrocarbons and thiophenes under visible light irradiation, using aqueous hydrogen bromide as the Br source and oxygen as the oxidant.
A number of bromination protocols use elemental bromine and N-bromosuccinimide as the Br sources, but these are toxic, hazardous and can over-brominate, producing mixtures. The photocatalytic reaction will enable scientists to synthesise brominated compounds on a large scale without the cost of isolation and purification.
Find out more by downloading Fukuzumi’s Chemical Science Edge article for free.