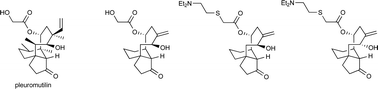
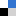US scientists have made new pleuromutilin-like compounds that show promise as leads for the development of new antibiotics. Erik Sorensen and colleagues made the compounds in approximately 11 steps from 3-allylcyclopent-2-enone by a strategy featuring sequential carbonyl addition reactions.
They found that the compounds displayed activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
‘As we move forward in our effort to expand the structural and stereochemical diversity of the pleuromutilin class of antibiotics, there is a high likelihood that we will discover additional, new compounds with promising activity against M. tuberculosis and possibly resistant strains of TB as well as other bacteria,’ say the team.
Download the article, which is free to access in Chemical Science.