Ice recrystallization inhibition (IRI) activity is a highly desirable property for an effective cryoprotectant. Cryopreservation is a very important process for regenerative medicine therapies, but ice recrystallization causes reduced post thaw cell viability. Although antifreeze proteins (AFPs) and antifreeze glycoproteins (AFGPs) were first investigated as cryoprotectants, their ability to bind and alter the ice crystals behaviour has encouraged researchers to look for further improvement in this field. This has led to the development of AFGP to AFGP analogues and further to the discovery of small carbohydrate-based IRIs with similar IRI activity to that of native AFGP-8.
In this review, Robert Ben and co-workers from the University of Ottawa, Canada, present recent developments of IRIs mainly focusing on novel small molecules that have emerged as potential cryoprotectants.
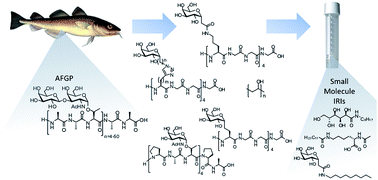
They begin with the molecular mechanism of the ice recrystallization phenomenon and it’s relation with IRI activities of biological antifreezes. The recent strategies for improving antifreeze compounds have been thoroughly discussed including large protein or peptide analogues, easily accessible synthetic polymers, simple mono- and disaccharide derivatives, truncated C-linked glycopeptides and carbohydrate or lysine-based surfactants/gelators. This review nicely highlights the importance of hydration index, relative orientation of hydrophilic groups and size of the linker of synthetic antifreeze compounds on their overall IRI activity.
In future these kinds of highly IRI active small molecules may replace the most widely used cytotoxic cryoprotectant DMSO and improve upon currently limited cryopreservation protocols.
Read the full review in RSC Advances – free to access for 4 weeks:
Designing ice recrystallization inhibitors: from antifreeze (glyco)proteins to small molecules
Anna K. Balcerzak, Chantelle J. Capicciotti, Jennie G. Briard and Robert N. Ben, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 42682-42696
You may also be interested in these related articles:
The importance of hydrophobic moieties in ice recrystallization inhibitors
Anna K. Balcerzak, Michela Febbraro and Robert N. Ben, RSC Adv., 2013, 3, 3232-3236
Developing highly active small molecule ice recrystallization inhibitors based upon C-linked antifreeze glycoprotein analogues
John F. Trant, Robyn A. Biggs, Chantelle J. Capicciotti and Robert N. Ben, RSC Adv., 2013, 3, 26005-26009
Comments Off on Does size matter? Rational design of potent ice recrystallization inhibitors