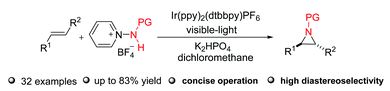
A group of researchers based at universities spanning the UK, China and Spain have synthesised a diverse library of fluorescent maleimide dyes with the aim of developing a structure-function relationship, relating substituent effects to the optical properties of such molecules. This work is not only important to build upon fundamental understanding of the fluorescence mechanism, but to develop knowledge that may be used to guide the synthesis of organic fluorophores which demand particular optical properties.
Organic fluorescent molecules are used as tools in many areas such as forensics, genetic analysis, DNA sequencing and biotechnology. Maleimides are commonly used as fluorescent labels for proteins, as they can couple with the thiol groups of cysteine residues. They are suited to this purpose as they are stable, easily functionalised, give strong emissions and do not perturb the protein structure to a large extent.
Molecules fluoresce upon absorption of UV or visible light, elevating an electron from a ground state orbital to a higher-energy orbital and resulting in a singlet excited state. Relaxation to the ground state occurs rapidly (~ 10 ns) with concomitant emission of a photon – this is what we observe as ‘fluorescence’. The emitted photon almost always has a longer wavelength than the absorbed light, a phenomenon known as the ‘Stokes shift’.
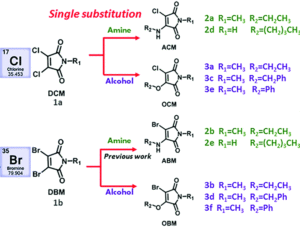
With three dihalomaleimide precursers in hand (Cl, Br and I) the researchers assembled a library of amino-halo-maleimides, amino-alkoxy-maleimides, and amino-thio-maleimides. They varied the R groups bound to the N, O and S heteroatoms to include aliphatic, phenyl and benzyl examples.
The optical properties of the amino-halo-maleimides in diethyl ether were examined and the emission wavelengths were measured to be 461-487 nm, giving green-blue fluorescence. The fluorescence quantum yields, a measure of the quantity of emitted photons compared to absorbed photons and an indication of emission brightness, decreased with the electronegativity of the halide (Cl: 37%, Br: 30%, I: 8%). Like many fluorescent molecules in solution the compounds exhibited solvafluorochromism: when the polarity of the solvent alters the optical properties. In protic solvents (methanol and water) the fluorescence quantum yields decreased to below 1% and the emission wavelengths increased by 73-109 nm. On the other hand, in non-polar solvents (cyclohexane) the fluorescence quantum yield increased, up to 56% for the chloro analogue.
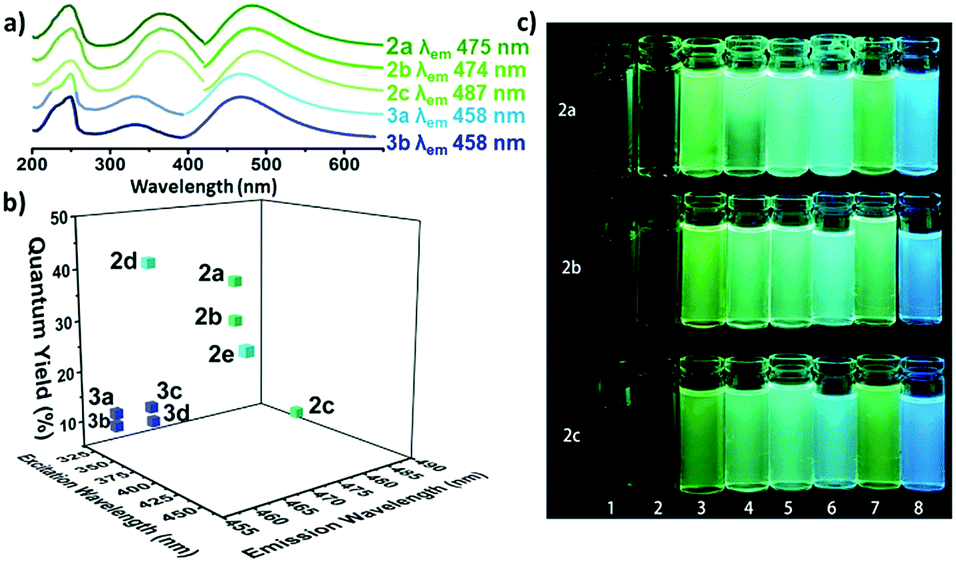
a) The UV and emission spectra of fluorescent maleimides bearing amino (2a-c) and alkoxy (3a, 3b) substituents. b) The quantum yields of selected amino and alkoxymaleimides. c) The solvafluorochromism effect for three maleimides (2a-c) in various solvents.
Compared to their amino-substituted counterparts, alkoxy-halo-maleimides have lower quantum yields (reduction of 20-25%), indicating the increased electron-donating capacity of the amine substituent is important for fluorescence intensity. Furthermore, the slight decrease in the emission wavelengths of alkoxy-halo-maleimides (458-465 nm) gives them blue fluorescent emissions. Amino-thio-maleimides, with greater electron-donating capacity than both the amino and alkoxy analogues, have increased emission wavelengths (526-564 nm), thus yellow fluorescent emissions.
This study is a worthwhile read for anyone who uses fluorescent molecules in their work, those wishing to understand a little more about the practical principles of fluorescence and all those curious minds who like to form their own hypotheses.
To find out more please read:
Rational design of substituted maleimide dyes with tunable fluorescence and solvafluorochromism
Yujie Xie, Jonathan T. Husband, Miquel Torrent-Sucarrat, Huan Yang, Weisheng Liu, Rachel K. O’Reilly.
Chem. Commun., 2018, 54, 3339 – 3342
DOI: 10.1039/C8CC00772A
 About the author:
About the author:
Zoë Hearne is a PhD candidate in chemistry at McGill University in Montréal, Canada, under the supervision of Professor Chao-Jun Li. She hails from Canberra, Australia, where she completed her undergraduate degree. Her current research focuses on transition metal catalysis to effect novel transformations, and out of the lab she is an enthusiastic chemistry tutor and science communicator.






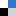




![Synthesis of oxazolines from ketones and isocyanaoacetate esters via a formal [3+2] cycloaddition reaction catalysed by a multicatalytic system of silver and a dihydroquinine squaramide organocatalyst](https://blogs.rsc.org/cc/files/2018/04/Screenshot-2018-04-03-16.24.41-300x171.png)
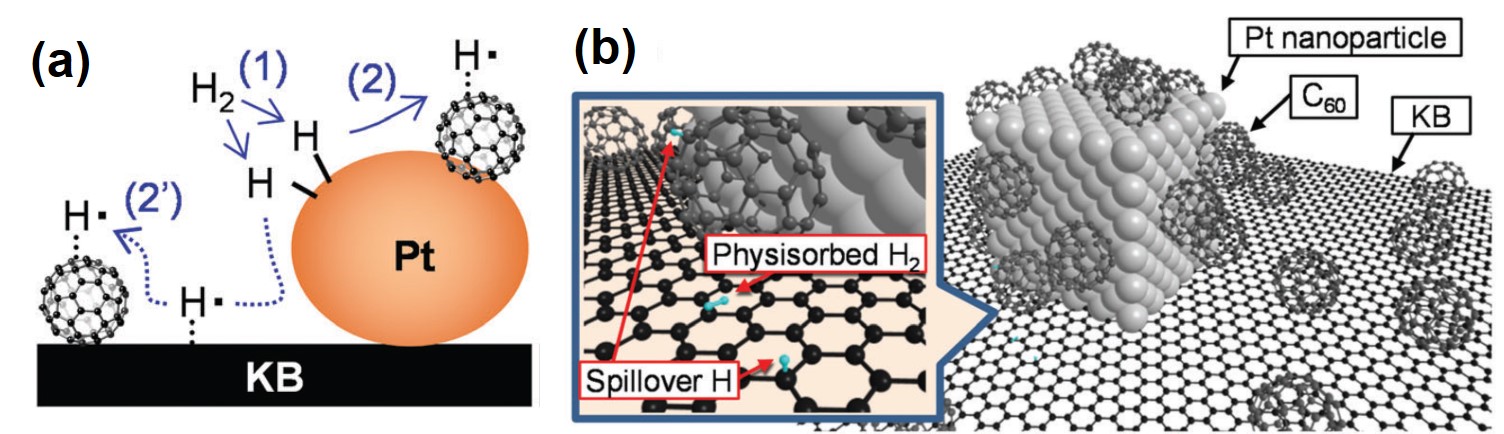
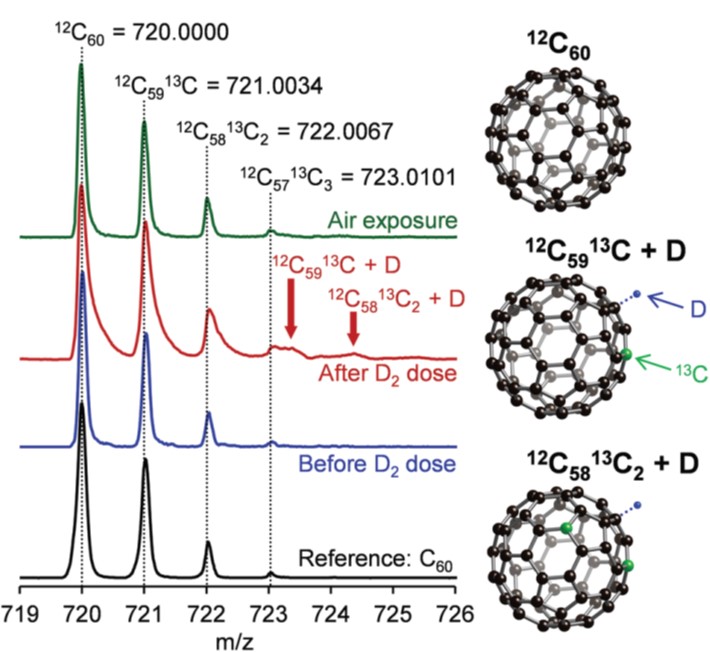
 Tianyu Liu obtained his Ph.D. (2017) in Physical Chemistry from University of California, Santa Cruz in United States. He is passionate about scientific communication to introduce cutting-edge research to both the general public and scientists with diverse research expertise. He is a blog writer for Chem. Commun. and Chem. Sci. More information about him can be found at
Tianyu Liu obtained his Ph.D. (2017) in Physical Chemistry from University of California, Santa Cruz in United States. He is passionate about scientific communication to introduce cutting-edge research to both the general public and scientists with diverse research expertise. He is a blog writer for Chem. Commun. and Chem. Sci. More information about him can be found at 
 ____________________________________________________
____________________________________________________