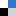Two porous supramolecular isomeric frameworks have shown unique sorption properties, say a collaboration of Chinese and Japanese scientists.
One framework shows temperature dependent and selective sorption of CO2, while the other framework shows gas uptake capacity for CO2, N2, H2 and CH4 at low temperature and selective sorption of CO2 over N2 around room temperature. Wei-Yin Sun and colleagues believe that the results provide useful guidance for improving metal organic framework (MOF) designs for gas storage and separation techniques.
Find out more, by reading the research results published in ChemComm. This article has been made free to access until the 13th May 2011, so why not download the communication today?