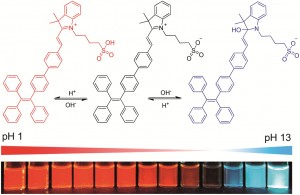
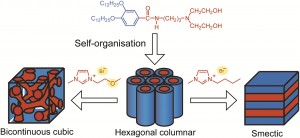
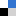Chemical Science and ChemComm are delighted to be sponsoring the New Frontiers in Stimuli-Responsive Supramolecular Assemblies symposium at the ACS spring meeting in San Diego.
To celebrate this fantastic symposium, Chemical Science is giving free access to some recent articles from a selection of the symposium’s guest speakers. Why not check out why they choose to publish with Chemical Science?
Cell surface-based differentiation of cell types and cancer states using a gold nanoparticle-GFP based sensing array
Avinash Bajaj, Subinoy Rana, Oscar R. Miranda, Joseph C. Yawe, D. Joseph Jerry, Uwe H. F. Bunz and Vincent M. Rotello, Chem. Sci., 2010, 1, 134-138
Cylindrical micelles from the living crystallization-driven self-assembly of poly(lactide)-containing block copolymers
Nikos Petzetakis, Andrew P. Dove and Rachel K. O’Reilly, Chem. Sci., 2011, 2, 955-960
A programmable transducer self-assembled from DNA
Banani Chakraborty, Natasha Jonoska and Nadrian C. Seeman, Chem. Sci., 2012, 3, 168-176
A mechanistic study of Lewis acid-catalyzed covalent organic framework formation
Eric L. Spitler, Marissa R. Giovino, Sarah L. White and William R. Dichtel, Chem. Sci., 2011, 2, 1588-1593
Cell-compatible, integrin-targeted cryptophane-129Xe NMR biosensors
Garry K. Seward, Yubin Bai, Najat S. Khan and Ivan J. Dmochowski, Chem. Sci., 2011, 2, 1103-1110
This content will be free to access until 1st April.