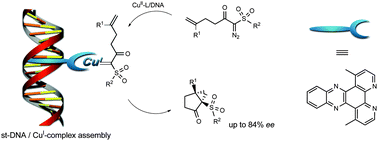
Scientists studying organometallic catalysts attached to DNA have used the technology to perform cyclopropanation reactions in water, and have reported efficient yields and high enantiomeric excesses.
By attaching the catalytically active metal complex to a DNA scaffold, the chirality of the DNA helix can be directed toward the reaction, influencing its outcome.
You can read this article for free for a limited period:
DNA-based asymmetric organometallic catalysis in water
Jens Oelerich and Gerard Roelfes
Chem. Sci., 2013, DOI: 10.1039/C3SC00100H