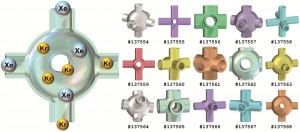
US scientists have applied high-throughput computational methods to explore thousands of possible (existing and hypothetical) MOF structures for separating krypton from xenon (selectively adsorbing Xe from a Xe/Kr mixture).
Xe and Kr are valuable gases, used in medical applications and lighting, but they are not straightforward to obtain as pure elements. These results should provide the MOF synthesis community with some new ideas for tailoring synthetic routes for specific gas adsorption/separation applications.
Link to journal article
Thermodynamic analysis of Xe/Kr selectivity in over 137,000 hypothetical metal-organic frameworks
B J Sikora et al
Chem. Sci., 2012, DOI: 10.1039/c2sc01097f