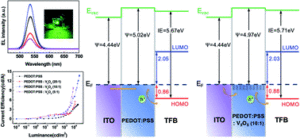
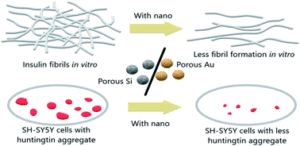
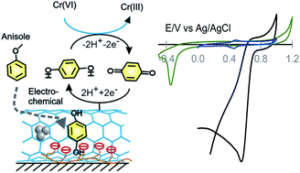
We are delighted to share with you our latest collection of recently published articles focusing on Metals in Medicine, handpicked by Associate Editor Dr. Camilla Abbehausen (University of Campinas).
This exciting research field explores all the periodic table diversity to design molecules, particles, and materials for diagnosis and treatment. After more than fifty-five years of cisplatin antitumor activity discovery and its tremendous impact in medicine, the collection shows how the field has expanded. The selection demonstrates strategies for tailoring the properties of metal complexes, metal nanoparticles, and inorganic materials by using coordination chemistry and nanotechnology.
Novel metallodrug designs continue to be exciting as innovative synthetic strategies of functionalization generate safer and more effective drugs. Their mechanistic investigation is also along with these contributions. Photodynamic and photothermal therapy gained strength as metals can provide the main characteristics for a successful agent. Metallo nanoparticles also present several applications as they can star in therapy and diagnostics or be a platform for drug delivery. Moreover, metallo-organic framework (MOFs) also figures in the advanced delivery systems. This edition envisages giving a taste of the diversity and impact of Metals in Medicine.
As the world’s largest gold open access chemistry journal, all publications in RSC Advances are free to access. We hope you enjoy reading these articles.
We invite you to submit your research to this collection and give your work the global visibility it deserves.
Featured articles:
Minerals in biology and medicine
Oliver W. L. Carter, Yingjian Xu and Peter J. Sadler
RSC Adv., 2021,11, 1939-1951. DOI: 10.1039/D0RA09992A
Iron and copper complexes with antioxidant activity as inhibitors of the metastatic potential of glioma cells
Joana F. Guerreiro, Joao Seco et al.
RSC Adv., 2020,10, 12699-12710. DOI: 10.1039/D0RA00166J
Biogenesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Pandanus odorifer leaf extract: anticancer and antimicrobial activities
Afzal Hussain, Mohamed F. Alajmi, Imran Ali et al.
RSC Adv., 2019,9, 15357-15369. DOI: 10.1039/C9RA01659G
Meet the Editor
 Camilla Abbehausen received her Bachelor’s degree in Chemistry from the University of Campinas in 2003 and was honored by the Regional Chemistry Council Prize for Bachelors in the same year. Before diving into academics, she worked from 2002 – 2010 at Dow Corning Co. in the Application Development and Research department to develop health and personal care applications for silicone polymers. In 2007 she received an Application Services – Latin America award for the services developed. Camilla received a Master’s degree in Inorganic Chemistry from the University of Campinas in 2009 and a Ph.D. from the same University in 2014. In a collaboration with Virginia Commonwealth University, under the supervision of Prof. Pedro Paulo Corbi and Prof. Nicholas Farrell, she studied the interaction of metal complexes with zinc finger domains and the development of metal-based antitumor, antiviral and antibacterial agents. Camilla was selected as Assistant Professor at the University of Campinas in 2015 and started a group on bioinorganic and medicinal inorganic chemistry. Camilla acted as a visiting professor at the Technical University of Munich (2020).
Camilla Abbehausen received her Bachelor’s degree in Chemistry from the University of Campinas in 2003 and was honored by the Regional Chemistry Council Prize for Bachelors in the same year. Before diving into academics, she worked from 2002 – 2010 at Dow Corning Co. in the Application Development and Research department to develop health and personal care applications for silicone polymers. In 2007 she received an Application Services – Latin America award for the services developed. Camilla received a Master’s degree in Inorganic Chemistry from the University of Campinas in 2009 and a Ph.D. from the same University in 2014. In a collaboration with Virginia Commonwealth University, under the supervision of Prof. Pedro Paulo Corbi and Prof. Nicholas Farrell, she studied the interaction of metal complexes with zinc finger domains and the development of metal-based antitumor, antiviral and antibacterial agents. Camilla was selected as Assistant Professor at the University of Campinas in 2015 and started a group on bioinorganic and medicinal inorganic chemistry. Camilla acted as a visiting professor at the Technical University of Munich (2020).
Her interests are the development of metal-based compounds for medical applications, especially in the interaction of these compounds with biomolecules and the studies of their mechanism of action. She is also studying metalloenzyme mechanism and inhibition, and developing novel methodologies for the synthesis of transition metal coordination compounds.

Submit to RSC Advances today! Check out our author guidelines for information on our article types or find out more about the advantages of publishing in a Royal Society of Chemistry journal.
Keep up to date with our latest HOT articles, Reviews, Collections & more by following us on Twitter. You can also keep informed by signing up to our E-Alerts.












 Dr. Carmen Gomes is currently an Associate Professor in the Mechanical Engineering Department at Iowa State University where she is leading a successful research program on the design of novel nanoscale materials using carbon-based nanomaterials and polymers for food safety and agricultural applications. Projects pursued in her laboratory range from fabrication of polymeric nanomaterials and nanostructured devices for biosensors to bioactive delivery systems. Dr. Gomes has over 14 years of experience working in the research area of nanotechnology applied to food processing, food safety and food quality to develop effective solutions in food and agriculture production.
Dr. Carmen Gomes is currently an Associate Professor in the Mechanical Engineering Department at Iowa State University where she is leading a successful research program on the design of novel nanoscale materials using carbon-based nanomaterials and polymers for food safety and agricultural applications. Projects pursued in her laboratory range from fabrication of polymeric nanomaterials and nanostructured devices for biosensors to bioactive delivery systems. Dr. Gomes has over 14 years of experience working in the research area of nanotechnology applied to food processing, food safety and food quality to develop effective solutions in food and agriculture production.
 Dr. Yu Wang is an Assistant Professor of Food Chemistry at the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department and Citrus Research and Education Center, University of Florida. Dr. Wang’s research mainly focuses on flavor chemistry and natural product chemistry, emphasizing the flavor (aroma and taste) of fruits, herbs and other agricultural commodities, and use of citrus by-product for health benefits. She got her PhD in Food Chemistry, at Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey. Dr. Wang had her postdoc. training at Massachusetts Institute of Technology focusing on “Omics” techniques for early diagnosing inflammation bowel disease (IBD). Dr. Wang received the Alexander von Humboldt Fellowship to work in the Chair of Food Chemistry and Molecular Sensory Science at the Technical University of Munich. Her research experience includes flavor chemistry, sensory science and food/plant metabolomics. Before joining University of Florida, Dr. Wang was a Flavor Chemist at Mars Chocolate Inc, working in global R&D directing flavor application, developing novel flavor profiles, analyzing cocoa and chocolate flavor, setting up flavor training program, and providing technical guidance.
Dr. Yu Wang is an Assistant Professor of Food Chemistry at the Food Science and Human Nutrition Department and Citrus Research and Education Center, University of Florida. Dr. Wang’s research mainly focuses on flavor chemistry and natural product chemistry, emphasizing the flavor (aroma and taste) of fruits, herbs and other agricultural commodities, and use of citrus by-product for health benefits. She got her PhD in Food Chemistry, at Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey. Dr. Wang had her postdoc. training at Massachusetts Institute of Technology focusing on “Omics” techniques for early diagnosing inflammation bowel disease (IBD). Dr. Wang received the Alexander von Humboldt Fellowship to work in the Chair of Food Chemistry and Molecular Sensory Science at the Technical University of Munich. Her research experience includes flavor chemistry, sensory science and food/plant metabolomics. Before joining University of Florida, Dr. Wang was a Flavor Chemist at Mars Chocolate Inc, working in global R&D directing flavor application, developing novel flavor profiles, analyzing cocoa and chocolate flavor, setting up flavor training program, and providing technical guidance.