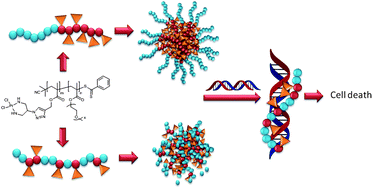
In this article, Stenzel and co-workers designed three different macromolecular Pt-drugs using Cu-click chemistry to attach a bidentate amino ligand to the polymer. Two statistical copolymers with different ligand densities were prepared, which were compared to the block copolymer. DNA binding studies revealed that the statistical copolymer with the highest density of Pt-drugs had the highest affinity to the DNA, due to a multivalent effect. Interestingly, when evaluating the cytotoxic effect of these macromolecular drugs using OVCAR-3 cells the activities of all three polymer architectures were similar. It can therefore be concluded that although DNA binding tests may give an initial indication on the ability of the structure to bind to the DNA, they cannot predict the outcome.
Macromolecular platinum-drugs based on statistical and block copolymer structures and their DNA binding ability by Khairil Juhanni Abd Karim, Sandra Binauld, Wei Scarano and Martina H. Stenzel Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 5542-5554.
Julien Nicolas is a guest web-writer and advisory board member for Polymer Chemistry. He currently works at Univ. Paris-Sud (FR) as a CNRS researcher.