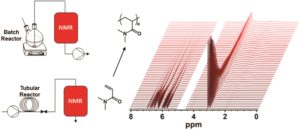
To precisely engineer macromolecular materials, close monitoring of the polymerization progress is required. Therefore, real-time online monitoring provides polymer chemists the opportunity to accurately observe and optimize their reactions. To this end, Warren and co-workers utilized benchtop flow-nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) as a very convenient and powerful tool for real-time monitoring of polymers synthesized either by controlled radical polymerization or free radical polymerization protocols. In particular, reversible addition-fragmentation chain-transfer (RAFT) polymerization was employed to polymerize acrylamides giving very high conversions in less than 10 minutes and the kinetic profile of this reaction was efficiently captured. In a second example where RAFT dispersion polymerization was monitored. In spite of the rapid polymerization rates, high temporal resolution enabled the previse determination of the onset of rate acceleration usually observed for polymerization induced self-assembly (PISA) systems. In addition to the monitoring of the aforementioned complex systems, the free radical polymerization of methyl methacrylate was also studied. In this case, the linear semi-logarithmic plot indicated the expected pseudo-first order kinetics. The results discussed here demonstrate the power of using benchtop NMR spectrometers for online flow applications where both controlled and free radical polymerizations can be employed. It is the author’s opinion that the lower price of these instruments will improve access to NMR spectroscopy while the reduced sample preparation/time taken for analysis will increase research output.
Tips/comments directly from the authors:
- Despite the reduced field strength, detailed polymerization kinetics comparable to traditional ‘high field’ NMR can be obtained since the vinyl protons are easily resolved.
- Flow-NMR is a powerful tool to improve time-resolution and reduce lab workload but must be used with care – e.g. flow rate and sample cell geometry must be optimized.
- Hydrogenated solvents can be used with lower-field instruments, but solvent selection is important: minimising any potential solvent overlap is key to reliable data.
- Spectral corrections such as to the phase and baseline are crucial for reliable data – especially if using an automated system.
Read the full article now for FREE until 8th November!
Benchtop flow-NMR for rapid online monitoring of RAFT and free radical polymerisation in batch and continuous reactors, Polym. Chem., 2019, 10, 4774-4778, DOI: 10.1039/C9PY00982E
About the web writer
 Dr. Athina Anastasaki is an Editorial Board Member and a Web Writer for Polymer Chemistry. Since January 2019, she joined the Materials Department of ETH Zurich as an Assistant Professor to establish her independent research group.
Dr. Athina Anastasaki is an Editorial Board Member and a Web Writer for Polymer Chemistry. Since January 2019, she joined the Materials Department of ETH Zurich as an Assistant Professor to establish her independent research group.