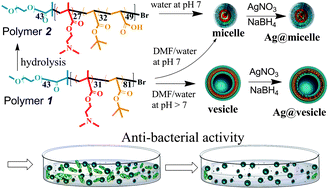
It is well known that silver nanoparticles have excellent antibacterial activities. However, to prepare well-defined, water-dispersible and long-term stable silver nanoparticles still remains a challenge. Presented in this paper are the design and preparation of new water-dispersible silver-decorated polymer vesicles and micelles based on a new kind of amphiphilic block-statistical copolymer synthesized by ATRP: poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate-stat-t-butyl acrylate) (PEO-b-P(DMA-stat-tBA)) and its partially hydrolyzed derivative, poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate-stat-acrylic acid) (PEO-b-P(DMA-stat-AA)). Poly(DMA) is introduced for the coordination of Ag+ ions to form silver nanoparticles in situ upon reduction, whereas poly(AA) is designed to serve the scaffold for the silver nanoparticle formation in the micelle core by electrostatic interactions with Ag+ ions. Those water-dispersible silver-decorated polymer micelles and vesicles showed excellent antibacterial efficacy against Escherichia coli (E. coli) with quite low minimum inhibitory concentration and minimum bactericidal concentration.
Preparation of water-dispersible silver-decorated polymer vesicles and micelles with excellent antibacterial efficacy by Hang Lu, Lang Fan, Qiuming Liu, Jingren Wei, Tianbin Renand Jianzhong Du Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 2217-2227.
To keep up-to-date with all the latest research, sign up for the journal’s e-alerts or RSS feeds or follow Polymer Chemistryon Twitter or Facebook.