Be sure to read our latest Editor’s Choice article as chosen by Associate Editor Jean-Louis Reymond!
This article is free-to-access until 8th November and can be found alongside our previously chosen articles in our online Editor’s Choice web-collection!

“Heptylmannose-functionalized cellulose for the binding and specific detection of pathogenic E. coli” by Jean-Louis Reymond:
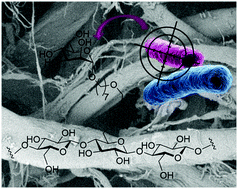
In their communication “Heptylmannose-functionalized cellulose for the binding and specific detection of pathogenic E. coli” Madeleine Cauwel et al. exploited the well-known FimH lectin system to devise a selective detection system for adherent-invasive E. coli (AIEC) involved in the pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease (CD). FimH is well known to bind mannosyl glycosides and to occur in AIEC. The trick here was to prepare a modified cellulose (as nanofiber or paper) using click chemistry, profile its lectin binding with state-of-the art chip analysis, verify its ability to block binding of AIEC from a CD patient to intestinal epithelial cells and to decrease AIEC levels in gut microbiota in a murine model, and finally to show that the modified paper binds selectively to pathogenic AIEC but not to benign E. coli.
Simple but effective chemistry, thorough experiments with relevant samples, impressive results. Chemical biology at its best.
Find our full Editor’s Choice collection online!
Keep up-to-date with our latest journal news on Twitter @ChemCommun or via our blog!
Learn more about ChemComm online! Submit your latest high impact research here!