The early detection and monitoring of disease is a somewhat recent advancement in healthcare that offers the significant advantage of being able to treat an illness in its initial stages, rather than once it has already manifested itself in the patient. Such a feat requires, however, the ability to see very specific and characteristic disease markers in situ, not unlike the search for a needle in a haystack.
Luckily, with the advent of fluorescence (and other) imaging techniques, methods have been developed whereby, in combination with contrast agents that are able to interact with specific molecules in the body, cell chemistry and function can be observed with high sensitivity, and, more importantly, abnormalities in these processes noticed in real time.
The art and ultimate success of this fluorescence imaging comes from the design of the contrast agent employed – the probe should be able to selectively recognise and target the relevant disease marker reversibly and under biological conditions. A number of approaches currently exist that meet these requirements, one of which is the boronic acid recognition motif that is able to act as a molecular receptor for the 1,2- and 1,3-diols commonly expressed in carbohydrates and complex glycoproteins. Tony James and his team from the University of Bath, whose own research focuses on such use of boronic acid receptors in the detection of carbohydrates, have summarised the recent and exciting advances in this particular field of selective biological imaging.
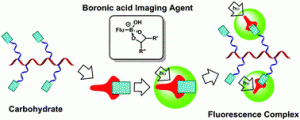 The well-known and strong affinity of boronic acids for carbohydrates offers a convenient means of detecting commonly expressed markers in diseases including some cancers, as well as Alzheimer’s, autoimmune, and heart diseases. As such, the attachment of this relatively simple chemical moiety to fluorescent small molecular, polymeric or benzoxaborale-based probes offers a diagnostic tool that is able to detect, monitor, and aid in the personalised treatment of such significant and life-changing diseases.
The well-known and strong affinity of boronic acids for carbohydrates offers a convenient means of detecting commonly expressed markers in diseases including some cancers, as well as Alzheimer’s, autoimmune, and heart diseases. As such, the attachment of this relatively simple chemical moiety to fluorescent small molecular, polymeric or benzoxaborale-based probes offers a diagnostic tool that is able to detect, monitor, and aid in the personalised treatment of such significant and life-changing diseases.This Feature Article convincingly highlights the impact that boronic acid-based fluorescence imaging will ultimately have on a range of important clinical and theranostic practices and their successes.
Read this hot ChemComm article in full:
X. Sun, W. Zhai, J. S. Fossey and T. D. James
Chem. Commun., 2016, 52, 3456–3469
DOI: 10.1039/C5CC08633G
About the Writer:
 Anthea Blackburn is a guest Web Writer for Chemical Communications. Anthea hails from New Zealand, carried out her graduate studies in mechanostereochemistry under the guidance of Prof. Fraser Stoddart in the US, and has recently relocated to live in London. She is a recent addition to the Econic Technologies team, where she is working on the development of new catalysts for the environmentally beneficial preparation of polycarbonates from CO2.
Anthea Blackburn is a guest Web Writer for Chemical Communications. Anthea hails from New Zealand, carried out her graduate studies in mechanostereochemistry under the guidance of Prof. Fraser Stoddart in the US, and has recently relocated to live in London. She is a recent addition to the Econic Technologies team, where she is working on the development of new catalysts for the environmentally beneficial preparation of polycarbonates from CO2.