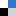We are all aware how important it is to find new improved ways to generate sustainable energy. One very promising candidate is the dye-sensitised solar cell which is particularly attractive due to its low production cost and mechanical robustness.
Scientists from East China Normal University have found a way to increase the efficiency of dye-sensitised solar cells by introducing an additional layer on top of the TiO2 photoanode. The extra layer, made up of Y3Al5O12:Ce down-converting microparticles, causes the conversion efficiency to increase from 6.97% to 7.91%.
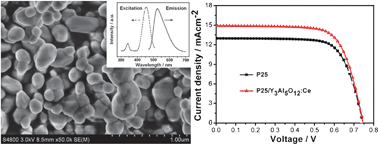
SEM image of the Y3Al5O12:Ce layer and the J-V curves for the solar cell with and without the additional layer
Likun Pan and his team have attributed this improved performance to the increased light absorbing and scattering properties of the microparticle layer (meaning more suitable photons are available for absorption by the dye) and reduced electron transfer resistance.
Download the ChemComm article to read more about the fabrication of Pan’s solar cell device.