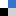The group of Dr. Lin Zhou have a research interest in Schizophyllan (SPG). As a biological macromolecule polysaccharide, SPG demonstrates good biological activity such as anti-tumor, anti-aging, antioxidant and moisturizing etc. The large molecular weight and high viscosity of SPG can also affect the level of dissolved oxygen in the later stage of fermentation, which limits the yield of SPG. In addition, separation and purification of SPG is time and cost intensive. The traditional herbal medicine contains great health value. Therefore, researchers have focused on the overall activity of the fermentation broth to expand the application of S. commune liquid fermentation.
In the article “Enhanced exopolysaccharide yield and antioxidant activities of Schizophyllum commune fermented products by the addition of Radix Puerariae“, the medicinal edible fungus Schizophyllum commune (S. commune) was used as the starting strain, and the traditional Chinese medicine Radix Puerariae (RP) was used as the medicinal substrate to expand the application of the S. commune fermentation liquids. The results showed that the addition of Pueraria did not affect the structure of Schizophyllan (SPG), the exopolysaccharide of S. commune, but the yield of SPG was significantly improved, which provided a theoretical basis for the industrial production of SPG. In addition, RP can also increase the antioxidant activity of the fermented supernatant from the S. commune fermentation system. These antioxidant activities mainly come from the puerarin from RP and some new ingredients that are synthesized during the fermentation process such as resveratrol. Therefore, this study proves the feasibility of the Schizophyllum liquid fermentation system as a bioreactor and provides a reference for the biotransformation of edible medicinal fungi such as Cordyceps militaris and Ganoderma lucidum etc.
Firstly, this research confirmed the feasibility of using the liquid fermentation of Schizophyllum commune as a biotransformer, and provided a reference for the expanded application of Schizophyllum commune and other medicinal and edible fungi. The results also shed light on the comprehensive utilization of traditional herbal medicine and plant substrates.
For the bidirectional fermentation system, monitoring of the fermentation process and evaluation of the biological activity of the fermentation products are the hotspots of future research. Follow up work about the anti-aging activity and underlying mechanisms of fermented S. commune by a Caenorhabditis elegans model will be reported in the near future.
I thank Dr. Lin Zhou for his cordial responses.
Read the article:
Enhanced exopolysaccharide yield and antioxidant activities of Schizophyllum commune fermented products by the addition of Radix Puerariae. Yongfei Deng, Qian Huang, Lu Hu, Tao Liu, Bisheng Zheng, Dengjun Lu, Chaowan Guo and Lin Zhou. RSC Adv., 2021, 11, 38219–38234.
About the web writer:
Cristian M. O. Lépori is a Doctor in Chemical Sciences and is currently a CONICET researcher at the Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto, Argentina. His research area is “Comprehensive approach through the articulation of knowledge and new strategies for the development of innovative products and processes applicable to health and the environment”. He likes to plan, organize and carry out science dissemination activities. You can find him on Twitter at @cristianlepo.