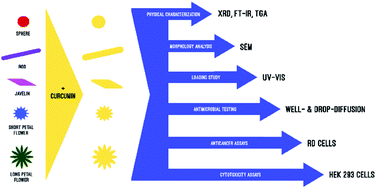
Treatment for cancer and bacterial infections is challenging to approach due to various reasons such as the development of resistant and unwanted side effects. Development of new chemotherapeutic agents often ends up with a blunt end. Therefore, finding a new formulation and an effective delivery method for the currently available agents is a gold alternative.
Curcumin and zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO Nps) are such compounds that have enormous advantages. Of the potent bioactive metabolites that have been identified from plant sources, curcumin is one of the most-investigated safe chemical compounds. Research over the last two decades has shown it to be a potent anticancer and antimicrobial agent in cell- and animal studies. But inheritably, curcumin has low efficacy mainly due to the poor bioavailability, contributed to by its insolubility, instability, poor absorption, and rapid biotransformation. ZnO Np is a well-investigated biocompatible and apparently nontoxic nanomaterial that has shown promising anticancer and antimicrobial activity as well. In the article “Curcumin loaded zinc oxide nanoparticles for activity-enhanced antibacterial and anticancer applications”, different shapes of curcumin loaded ZnO Nps were investigated for their effectiveness and safety as an anticancer and antibacterial agent. The results indicate that curcumin loaded ZnO Nps are low toxic and a highly effective combination compared with their bare counterparts. Moreover, since nanoparticles show different absorption mechanisms through the gastrointestinal tract, it is a good alternative to mask compound which has low absorption capacity. In this study, other than the synergetic effect of curcumin loaded Nps, ZnO Nps act as a carrier system for curcumin, which has bioavailability issues.
Of particular note is the potential of this platform to act as an antibiotic-free formulation for use against infections caused by a range of different bacterial pathogens. Given the anticancer activity of the platform, it may prove to be of great use as an oncotherapy supplement, helping manage both the disease condition and opportunistic bacterial infections. The findings of this research open doors for different angles of curcumin and ZnO Np research. Therefore, the responsibility of the scientists is to use this finding to develop appropriate dosage foam for curcumin loaded ZnO Np.
I thank Dr. Ranga K. Dissanayake for his cordial responses.
Read the article:
W. P. T. D. Perera, Ranga K. Dissanayake, U. I. Ranatunga, N. M. Hettiarachchi, K. D. C. Perera, Janitha M. Unagolla, R. T. De Silva and L. R. Pahalagedara. RSC Adv., 2020, 10, 30785–30795.
About the Web Writer:
 Cristian M. O. Lépori is Doctor in Chemical Sciences and currently has a postdoctoral position at the Instituto de Física Enrique Gaviola, CONICET – Universidad Nacional de Córdoba, Argentina. He works in the area of green chemistry. He likes to plan, organize and carry out science dissemination activities. You can find him on Twitter at @cristianlepo.
Cristian M. O. Lépori is Doctor in Chemical Sciences and currently has a postdoctoral position at the Instituto de Física Enrique Gaviola, CONICET – Universidad Nacional de Córdoba, Argentina. He works in the area of green chemistry. He likes to plan, organize and carry out science dissemination activities. You can find him on Twitter at @cristianlepo.
 Submit to RSC Advances today! Check out our author guidelines for information on our article types or find out more about the advantages of publishing in a Royal Society of Chemistry journal.
Submit to RSC Advances today! Check out our author guidelines for information on our article types or find out more about the advantages of publishing in a Royal Society of Chemistry journal.
Keep up to date with our latest HOT articles, Reviews, Collections & more by following us on Twitter. You can also keep informed by signing up to our E-Alerts.