A composite material contains two or more constituents which when combined afford significantly different material properties than the individual components. Well-known composites include concrete, plywood and fibre-reinforced plastics. With regard to polymeric composite materials, they usually consist of fillers dispersed in a polymer matrix to improve desired mechanical properties of the polymer material. Recently, research efforts have also focused on nanocomposites, where the filler has at least one dimension in the nano-scale, for example, nanoparticles, carbon nanotubes, 2D-sheets, such as graphene oxide, and nanofibres. These nano-fillers have shown huge improvements to material properties at low mass fractions, primarily due to the high surface area to volume ratio that nanomaterials possess. The increased interfacial area between the nanomaterial and continuous polymer matrix results in increased polymer-filler strength. Various applications have been proposed for nanocomposites: biomedical applications, waste water treatment, structural materials to name but a few.
Each of the highlighted articles this month report polymeric nanocomposites with improved properties such as increased strength, thermal stability, and desired adsorption behaviour when compared to the non-composite materials.
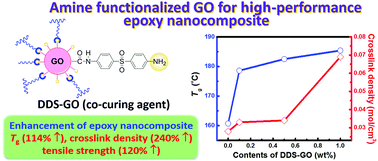
1. Enhancement of the crosslink density, glass transition temperature, and strength of epoxy resin by using functionalized graphene oxide co-curing agents, Jin Won Yu, Jin Jung, Yong-Mun Choi, Jae Hun Choi, Jaesang Yu, Jae Kwan Lee, Nam-Ho You, Munju Goh, Polym. Chem., 2016, 7, 36-43.
Graphene oxide (GO) was incorporated into epoxy resins through functionalisation of the edge of the GO with amino groups, subsequently utilised for reaction with epoxy groups present in the polymer matrix. The incorporation of the modified GO into the resin improved the tensile strength and thermal properties of the materials. Higher crosslinking densities were also observed due to the covalent linking of the GO thanks to the amino groups introduced.
2. Tailored high performance shape memory epoxy–silica nanocomposites. Structure design, S. Ponyrko, R. K. Donato, L. Matějka, Polym. Chem., 2016, 7, 560-572.
The authors describe the preparation of epoxy resins containing silica nanoparticles and shape memory behavior of the materials was investigated. The materials were prepared through in situ generation of nanosilica within the epoxy resin. The stimuli utilized for the shape memory behavior was temperature, exploiting the visco-elastic behavior of the epoxy resin. The results contribute to improved understanding of this type of shape memory materials.
3. A core–shell structure of polyaniline coated protonic titanate nanobelt composites for both Cr(VI) and humic acid removal, Tao Wen, Qiaohui Fan, Xiaoli Tan, Yuantao Chen, Changlun Chen, Anwu Xu, Xiangke Wang, Polym. Chem., 2016, 7, 785-794.
Core-shell polyaniline/hydrogen titanate nanobelt composites were prepared through in situ oxidative polymerisation which showed excellent absorption of Cr(VI) and humic acid for waste water treatment applications. The mechanisms of the Cr(VI) and humic acid removal were investigated as well as regeneration performance and reusability. The industrial implications on the composites appear promising; showing efficient and cost effective waste water treatment.
Dr. Fiona Hatton is a Web Writer for Polymer Chemistry. She is currently a postdoctoral researcher at KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden, having completed her PhD in the Rannard group at the University of Liverpool, UK. Visit her webpage for more information.