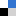Polymersomes that shed their poly(ethylene glycol) shell have been developed by scientists at Radboud University Nijmegen, The Netherlands.
The polymersomes are formed from block copolymers of polybutadiene-b-poly(ethylene glycol) coupled via an acid sensitive hydrazone moiety. The team found that the minimum amount of surface PEGylation needed to retain stable polymersomes was as low as five percent.
Interested to know more? Why not read the full article for free here: René P. Brinkhuis*, Taco R. Visser, Floris P. J. T. Rutjes and Jan C. M. van Hest, Polym. Chem., 2011, DOI:10.1039/C0PY00316F