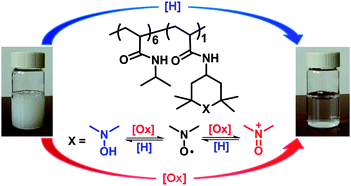
A team led by James Batteas and David Bergbreiter at Texas A&M University, USA, have designed “smart” acrylamide copolymers with reversible redox behaviour which changes lower critical solution temperature. The polymers are contain on N-isopropyl and 4-N-amino-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-oxyl-4-yl (TEMPO) groups. Oxidation or reduction varies the copolymer’s lower critical solution temperature from 18 °C to 35–40 °C.
The team say that these smart polymers could lead to the design of redox-sensitive materials for drug delivery applications in vivo or in the synthesis of surfaces with redox-mediated wettability.
To find out more, why not download the article today?