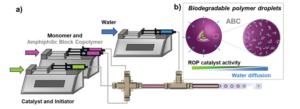
Harrier et al. highlight the encapsulation methodology as a readily available, efficient methodology to perform ROPs in aqueous dispersions.
Ring opening polymerizations (ROP) are widely used to synthesize a variety of biodegradable polymers typically under the strict limitations requiring anhydrous media and inert atmosphere (usually dictating the use of complex setups such as Schlenk lines or glove boxes). These practical limitations limit the polymeric material accessible by ROP.
To address this limitation, Guironnet and collaborators implemented a droplet microfluidic encapsulation strategy and systematically investigated both the process and the formulation parameters that govern the stability of the formed micro-droplets. The identification of these parameters together with the addition of amphiphilic block copolymers (PEG-PVL, PEG-PCL, and Pluronic) and a hydrophobe (hexadecane) allowed to control the viscosity, surface tension, and hydrophobicity of the formed droplets. As a result, the conditions in which the ROP catalyst was efficiently shielded in the aqueous dispersion could be identified and used to achieve higher monomer conversion and higher molecular weight polymers in the polymerization of valerolactone and caprolactone. By changing the amphiphilic block copolymer composition, ROP reaction time could also be further improved. To highlight the strength of this approach, these design rules were also used to tune the viscosity and surface tension of the droplets during ROP of propylene oxide catalyzed by an organic Lewis-Pair catalyst system (i.e. a phosphazene base and triethyl borane), leading to the synthesis of polyether particles dispersed in water.
In summary this study highlights the power and versatility of the encapsulation methodology applied with an off-the-shelf droplet-based microfluidic device and establish the fundamental guiding principles to encapsulate water-sensitive polymerization catalysts to efficiently synthesize spherical polymer particles dispersed in water.
Design rules for performing water-sensitive ring-opening polymerizations in an aqueous dispersion, Polym. Chem., 2022, 13, 2459-2468
Link to the paper: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2022/py/d2py00069e#cit11