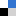Sophie Guillaume is a member of the Advisory Board for Polymer Chemistry and a CNRS Research Director at the Institut des Sciences Chimiques de Rennes (ISCR), France.
Sophie Guillaume is a member of the Advisory Board for Polymer Chemistry and a CNRS Research Director at the Institut des Sciences Chimiques de Rennes (ISCR), France.
Her research focuses on the development of green pathways for the synthesis and structure–property relationships of synthetic polymers (especially polyesters, polycarbonates, polyolefins, and polyurethanes). Areas of emphasis include biobased degradable polymers and functionalized and reactive (co)polymers for advanced industrial and biomedical applications.
You can find all Advisory Board’s Top Picks papers in our web collection.
Focus on polyurethanes
All articles are free to read until Sunday 5th March.
Polyurethanes (PUs) are one of the most important classes of polymeric materials most widely used as coatings, adhesives, sealants, foams, or elastomers. These multiblock copolymers are formed by the stepwise addition of diols (or polyols) with diisocyanates (or polyisocyanates). Efforts to reduce their environmental impact and to improve their sustainability, resulted in the development of biobased monomers, and of greener processes towards non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPUs). Original PU materials with properties at least matching or improving those of the current PU market are thus being sought. To this end, functionalization introduced via the amine segment, the polyol moiety, or the repeating units’ pending groups, is a key parameter to tune towards the desirable characteristics and targeted applications. The biomedical field provides further opportunities for biocompatible and biodegradable PU materials which are widely used as nerve tissue scaffolds, vascular prostheses or drug delivery systems. However, their physical properties (mechanical properties, degradation performances and blood compatibility) still require improvements. These present trends are illustrated with the following top-picks.
Alexander Yuen, Amaury Bossion, Enrique Gómez-Bengoa, Fernando Ruipérez, Mehmet Isik, James L. Hedrick, David Mecerreyes, Yi Yan Yang and Haritz Sardon
Polym. Chem., 2016, 7, 2105-2111
 Current efforts in the polyurethane (PU) community aim at developing green strategies exempt of the use of toxic and dangerous isocyanates. Nowadays, the most promising route towards such non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPUs) is the aminolysis of dicyclic carbonates. H. Sardon and co-workers at the University of the Basque Country (Spain), have synthesized, at room temperature without the need for any additional catalyst, high molar mass NIPUs (up to 47 kg.mol1) from a (bis) N-substituted eight-membered cyclic carbonate (N-8CC) derived from renewable resources using a variety of diamines. These experimental results highlight the unique reactivity of this N-8CC over the smaller five- and six-membered cyclic carbonates, as further supported by computational insights which revealed a kinetically and theoretically more favourable ring opening of the N-8CC by an amine system.
Current efforts in the polyurethane (PU) community aim at developing green strategies exempt of the use of toxic and dangerous isocyanates. Nowadays, the most promising route towards such non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPUs) is the aminolysis of dicyclic carbonates. H. Sardon and co-workers at the University of the Basque Country (Spain), have synthesized, at room temperature without the need for any additional catalyst, high molar mass NIPUs (up to 47 kg.mol1) from a (bis) N-substituted eight-membered cyclic carbonate (N-8CC) derived from renewable resources using a variety of diamines. These experimental results highlight the unique reactivity of this N-8CC over the smaller five- and six-membered cyclic carbonates, as further supported by computational insights which revealed a kinetically and theoretically more favourable ring opening of the N-8CC by an amine system.
Hiroyuki Matsukizonoa and Takeshi Endo
Polym. Chem., 2016, 7, 958-969
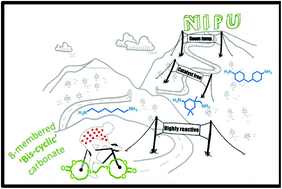
 Poly(hydroxyurethane)s (PHUs) derived from the polyaddition of six-membered ring cyclic carbonates with diamines are promising non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPUs) alternatives to polyurethanes (PUs), as evidenced by T. Endo and co-worker at Kinki University (Japan). Such PHUs advantageously contain two primary hydroxyl groups in their side chains of repeating units, which improve the hydrophilicity and which can be chemically modified to design functional PHU materials. Original well-defined water-soluble poly(carbonate–hydroxyurethane)s comprising hydroxyurethane–carbonate–hydroxyurethane alternate structures were synthesized from trimethylolpropane and conventional diamines. Investigations of their hydrolytic properties in aqueous media at different pH values revealed their complete decomposition to their basic structures in carbonate buffers at pH 10.6 within one week.
Poly(hydroxyurethane)s (PHUs) derived from the polyaddition of six-membered ring cyclic carbonates with diamines are promising non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPUs) alternatives to polyurethanes (PUs), as evidenced by T. Endo and co-worker at Kinki University (Japan). Such PHUs advantageously contain two primary hydroxyl groups in their side chains of repeating units, which improve the hydrophilicity and which can be chemically modified to design functional PHU materials. Original well-defined water-soluble poly(carbonate–hydroxyurethane)s comprising hydroxyurethane–carbonate–hydroxyurethane alternate structures were synthesized from trimethylolpropane and conventional diamines. Investigations of their hydrolytic properties in aqueous media at different pH values revealed their complete decomposition to their basic structures in carbonate buffers at pH 10.6 within one week.
Bio-based difuranic polyol monomers and their derived linear and cross-linked polyurethanes
Zehuai Mou, Shuo (Kelvin) Feng and Eugene Y. X. Chen
Polym. Chem., 2016, 7, 1593–1602
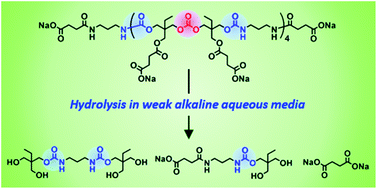
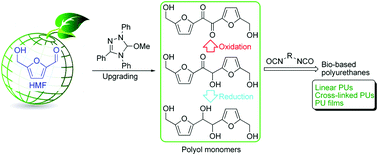 A series of linear and cross-linked polyurethanes (PUs) is reported by E. Chen and co-workers at Colorado State University (USA), from the catalysed polyadditions of diol, triol or tetraol derived from the biomass platform chemical 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) – one of the most value-added biomass building blocks or platform chemicals – with various diisocyanates in the presence of a catalyst (organocatalyst or dibutyltin dilaurate), respectively. The PU materials derived from the new diol monomer, namely 5,5’-bihydroxymethyl furil, and aromatic diisocyanates such as diphenylmethane diisocyanate, revealed valuable characteristics (Mn,SEC = ca. 40 kg mol−1, onset decomposition temperature = 234 °C, and Tg = 140 °C). Solvent casting from these PUs affords thin films ranging from brittle to flexible with a high strain at break of 300%.
A series of linear and cross-linked polyurethanes (PUs) is reported by E. Chen and co-workers at Colorado State University (USA), from the catalysed polyadditions of diol, triol or tetraol derived from the biomass platform chemical 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) – one of the most value-added biomass building blocks or platform chemicals – with various diisocyanates in the presence of a catalyst (organocatalyst or dibutyltin dilaurate), respectively. The PU materials derived from the new diol monomer, namely 5,5’-bihydroxymethyl furil, and aromatic diisocyanates such as diphenylmethane diisocyanate, revealed valuable characteristics (Mn,SEC = ca. 40 kg mol−1, onset decomposition temperature = 234 °C, and Tg = 140 °C). Solvent casting from these PUs affords thin films ranging from brittle to flexible with a high strain at break of 300%.
Stefan Mommer, Khai-Nghi Truong, Helmut Keul and Martin Möller
Polym. Chem., 2016, 7, 2291–2298
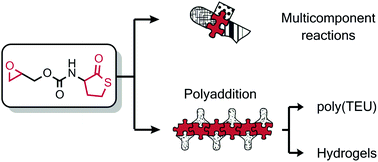 The synthesis of a new epoxy thiolactone is described by H. Keul and M. Möller and co-workers at RWTH Aachen University (Germany), along with its ability to act in several concepts as a versatile tool towards polymeric materials. The reactivity of this epoxy thiolactone with an amine and catalytic amounts of a base, results in the selective ring opening of the thiolactone to generate an AB-type epoxy thiol monomer, which in situ starts a thiol-epoxy polymerization to ultimately form poly(thioether urethane)s (PTEUs). Besides the introduction of a new functionality – the organic residue – by the amine used for ring opening of the thiolactone, the PTEU backbone further exhibits a hydroxyl functionality. The latter increases the hydrophilicity of the polymer backbone and also provides a site for an additional functionalization. Two strategies were elaborated for the generation of functional gels from this epoxy thiolactone bis cyclic monomer, using a diamine or a triacrylate. These one pot processes are feasible and provide an interesting platform for a variety of polymer architectures hosting functionalities.
The synthesis of a new epoxy thiolactone is described by H. Keul and M. Möller and co-workers at RWTH Aachen University (Germany), along with its ability to act in several concepts as a versatile tool towards polymeric materials. The reactivity of this epoxy thiolactone with an amine and catalytic amounts of a base, results in the selective ring opening of the thiolactone to generate an AB-type epoxy thiol monomer, which in situ starts a thiol-epoxy polymerization to ultimately form poly(thioether urethane)s (PTEUs). Besides the introduction of a new functionality – the organic residue – by the amine used for ring opening of the thiolactone, the PTEU backbone further exhibits a hydroxyl functionality. The latter increases the hydrophilicity of the polymer backbone and also provides a site for an additional functionalization. Two strategies were elaborated for the generation of functional gels from this epoxy thiolactone bis cyclic monomer, using a diamine or a triacrylate. These one pot processes are feasible and provide an interesting platform for a variety of polymer architectures hosting functionalities.
Cai Wang, Yudong Zheng, Yi Sun, Jinsheng Fan, Qiujing Qina and Zhenjiang Zhao
Polym. Chem., 2016, 7, 6120-6132
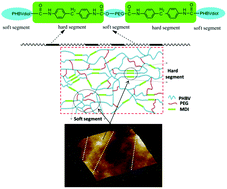 A novel block polyurethane (PU) based on poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV), 4,4’-diphenylmethanediisocyanate and poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) was synthesized by Zheng and co-workers at the University of Science and Technology Beijing (China), from the polyaddition of PHBV diol with ,-diisocyanate telechelic PEG. The resulting PU films exhibited biodegradability at 37 °C in phosphate buffer solution (PBS) at pH 7.4, non-cytotoxicity towards the growth and proliferation of the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, and hemocompatibility. The degradation rate results indicate that PHBV-based PUs are more suitable for biomedical applications requiring a longer degradation period. Greater PHBV contents also favourably influenced the mechanical properties and the thermal stability of these PU films. These new PHBV based PU materials with better mechanical properties, biodegradability, hemocompatibility and biocompatibility, may find potential applications in blood vessel tissue engineering.
A novel block polyurethane (PU) based on poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV), 4,4’-diphenylmethanediisocyanate and poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) was synthesized by Zheng and co-workers at the University of Science and Technology Beijing (China), from the polyaddition of PHBV diol with ,-diisocyanate telechelic PEG. The resulting PU films exhibited biodegradability at 37 °C in phosphate buffer solution (PBS) at pH 7.4, non-cytotoxicity towards the growth and proliferation of the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, and hemocompatibility. The degradation rate results indicate that PHBV-based PUs are more suitable for biomedical applications requiring a longer degradation period. Greater PHBV contents also favourably influenced the mechanical properties and the thermal stability of these PU films. These new PHBV based PU materials with better mechanical properties, biodegradability, hemocompatibility and biocompatibility, may find potential applications in blood vessel tissue engineering.
Thermo- and pH-sensitive shape memory polyurethane containing carboxyl groups
Qiuju Song, Hongmei Chen, Shaobing Zhou, Keqing Zhao, Biqing Wang and Ping Hu
Polym. Chem., 2016, 7, 1739-1746
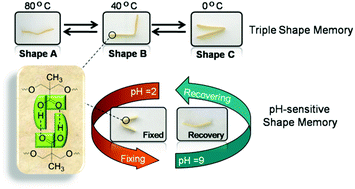 A multi-functional polyurethane (PU) with both a thermo-induced triple shape memory effect and a pH-sensitive dual shape memory effect has been developed by Chen and Hu and co-workers at Sichuan Normal University (China). The two-step polyaddition of polyethylene glycol (PEG), and 4,4’-diphenylmethane diisocyanate, followed by polymerization of the resulting diisocyanate end-functionalized PEG with dimethylolpropionic acid afforded the desired PUs bearing pendant carboxyl groups. In PU with 30wt% of PEG, the glass transition of PEG chains and the association/disassociation of carboxylic dimers act as two switches to control the triple-shape memory effect, while the carboxylic dimer is affected by pH values to associate in acidic solutions (pH 2) and dissociate in alkaline solutions (pH 9) to induce the pH-sensitive shape memory. The carboxylic dimers play an important role in the construction of shape memory properties in these PUs. Indeed, PUs with too high or too low carboxylic content (e.g. with 20 or 40wt% of PEG) did not exhibit any shape memory properties.
A multi-functional polyurethane (PU) with both a thermo-induced triple shape memory effect and a pH-sensitive dual shape memory effect has been developed by Chen and Hu and co-workers at Sichuan Normal University (China). The two-step polyaddition of polyethylene glycol (PEG), and 4,4’-diphenylmethane diisocyanate, followed by polymerization of the resulting diisocyanate end-functionalized PEG with dimethylolpropionic acid afforded the desired PUs bearing pendant carboxyl groups. In PU with 30wt% of PEG, the glass transition of PEG chains and the association/disassociation of carboxylic dimers act as two switches to control the triple-shape memory effect, while the carboxylic dimer is affected by pH values to associate in acidic solutions (pH 2) and dissociate in alkaline solutions (pH 9) to induce the pH-sensitive shape memory. The carboxylic dimers play an important role in the construction of shape memory properties in these PUs. Indeed, PUs with too high or too low carboxylic content (e.g. with 20 or 40wt% of PEG) did not exhibit any shape memory properties.