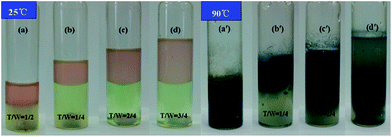
Zhu et al. applied Cu(II)-mediated atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) of methyl methacrylate (MMA) using the concept of thermoregulated phase-transfer catalysis (TRPTC) for an aqueous–organic biphasic system. Activators generated by electron transfer (AGET) ATRP was used to establish the TRPTC ATRP system using 2-cyanoprop-2-yl 1-dithionaphthalate (CPDN) as an alkyl pseudohalide initiator, CuBr2 as the catalyst and ascorbic acid (AsAc) as the reducing agent. They used a thermoresponsive monofunctional ligand including the dipyridyl group (MPEG-DPA), which enabled the transfer of the catalyst complex into the organic phase from the aqueous phase upon heating, thus achieving homogeneous polymerization; and the catalyst complex could retransfer into the aqueous phase from the organic phase thereby realizing the separation and recycling of the catalyst complex upon cooling. Well-defined PMMA with controlled molecular weight and narrow molecular weight distribution could be obtained by TRPTC ATRP. Furthermore, the polymerization of MMA could be successfully carried out even when the amount of catalyst was reduced to the ppm level. The features of controlled/“living” radical polymerization of MMA were verified by chain end analysis and chain-extension experiments.
Atom transfer radical polymerization of methyl methacrylate with a thermo-responsive ligand: construction of thermoregulated phase-transfer catalysis in an aqueous–organic biphasic system by Jinlong Pan, Lifen Zhang, Liangjiu Bai, Zhengbiao Zhang, Hong Chen, Zhenping Cheng* and Xiulin Zhu*, Polym. Chem., 2013, 4, 2876-2883.