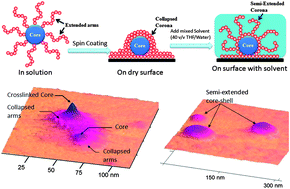
A facile approach for the preparation of well-controlled crosslinked core–corona (CCC) nanoparticles is described. Firstly, a core containing multiple initiating sites was generated by deactivation enhanced atom transfer radical homopolymerisation (DE-ATRP) of divinylbenzene (DVB). Then, the multiple halide initiating sites on this hyperbranched polyDVB core were used to initiate linear chains of methyl methacrylate (MMA) via ATRP. During the second step, the pendant vinyl groups within the core were consumed, leading to generation of a crosslinked nanogel core within the final polymer structures isolated, whilst linear arms (corona) were simultaneously growing from the periphery. The structure of the resulting CCC nanoparticles was confirmed using 1H NMR spectroscopy, gel permeation chromatography equipped with MALLS (GPC-MALLS), dynamic light scattering (DLS) and atomic force microscopy (AFM).
In situ formation of crosslinked core–corona polymeric nanoparticles from a novel hyperbranched core
Yu Zheng, Kristofer J. Thurecht, Xinyong Chen, Clive J. Roberts, Derek J. Irvine, Steven M. Howdle and Wenxin Wang
Polym. Chem., 2012, 3, 2807-2814.
To keep up-to-date with all the latest research, sign up for the journal’s e-alerts or RSS feeds or follow Polymer Chemistry on Twitter or Facebook.