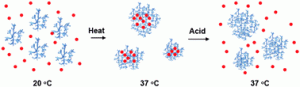
Hyperbranched poly(amine-ester)s that combine thermo-responsiveness and a highly branched structure, can be used to construct smart drug delivery systems claim scientists from Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China. The team led by Xinyuan Zhu and Bangshang Zhu synthesized the hyperbranched polymers with a one-pot through proton-transfer polymerization of triethanolamine, trimethylolpropane, and glycidyl methacrylate using potassium hydride as a catalyst. The team used the hyperbranched polymers to encapsulate the anticancer drug doxorubicin and then tested the effectiveness of the release of the drug in cells.
To keep up-to-date with all the latest research, sign up for the journal’s e-alerts or RSS feeds or follow the Polymer Chemistry on Twitter or Facebook.