Jun Di, Jiexiang Xia,* Mengxia Ji, Li Xu, Sheng Yin, Zhigang Chen and Huaming Li*
J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C6TA00284F
Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots (N-CQDs) modified atomically-thin BiOI nanosheets nanojunctions have been controllably prepared. The obtained BiOI consisted of 1–2 [Bi–O–I] units, which is the thinnest BiOX material reported so far. The atomically-thin structure was designed to accelerate carrier transfer among the BiOI nanosheet interior while the N-CQDs were constructed to facilitate surface charge carrier separation. Bidirectional acceleration of carrier separation can be achieved via this unique structure for both the materials interior and the surface.
Recently microneedles have been explored for transdermal monitoring of biomarkers with the goal to achieve time-sensitive clinical information for routine point-of-care health monitoring. In this highlight we provide a general overview of recent progress in microneedle-based sensing research, including: (a) glucose monitoring, (b) ex vitro microneedle diagnostic systems for general health monitoring with an emphasis on sensor construction, and (c) in vivo use of microneedle sensors.
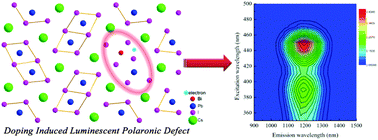
Bismuth doped materials with near infrared (NIR) photoluminescence (PL) have recently attracted tremendous attention because of their great potential for photonic and optoelectronic devices that could find broad applications in modern optical telecommunications. However, the mechanistic studies of the NIR PL from these materials still significantly lag behind, which imposes substantial limitations in rationally discovering and designing new materials. In this contribution, we investigated the optical and structural properties of Bi doped CsPbI3 using a diverse range of experimental techniques.