US scientists have developed a separator gel that can form a permanent barrier between blood components when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light, to keep cells and plasma apart for medical analysis.
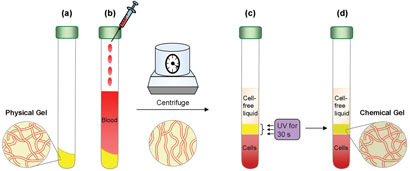
(a) The gel is placed at the bottom of a tube. (b) A blood sample is added. The tube is then placed in a centrifuge, where the gel is liquefied. Owing to its density, the liquefied gel flows to a position between the blood cells and plasma. (c) When centrifugation is stopped, the network is re-established and the gel recovers its solid character, forming a weak barrier between the blood layers. (d) The gel layer is irradiated with a UV lamp, converting the material into a hard, chemically crosslinked network, resulting in a rigid and permanent barrier
Blood tests typically only use the cell-free fraction of whole blood (serum or plasma), and it is common practice within blood sample tubes for these liquids to be separated from the blood cells by a separator gel. Separator gels are designed to reversibly liquefy during centrifugation. They have a density between that of the cells and solution components, so that they separate the components by flowing to a position between the layers during centrifugation. Following centrifugation, the gels stop flowing and remain as a soft barrier between the layers. However, the soft barrier can cause contamination, and leaks between the components and the gel can occur during sample transportation and storage. Interested to know more? Read the full article in Chemistry World here…
A new method for centrifugal separation of blood components: Creating a rigid barrier between density-stratified layers using a UV-curable thixotropic gel
Kunshan Sun, Hyuntaek Oh, Jane F. Emerson and Srinivasa R. Raghavan
J. Mater. Chem., 2012, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C2JM14818H
To keep up-to-date with all the latest research, sign up for the journal’s e-alerts or RSS feeds or follow Journal of Materials Chemistry on Twitter










