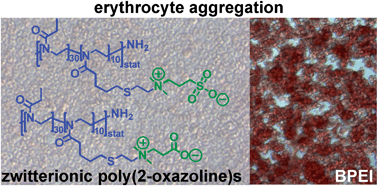
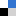The synthesis of highly hemo- and cytocompatible zwitterionic 2-oxazoline-based poly(sulfobetaine)s and poly(carboxybetaine)s, which demonstrate beneficial anticoagulant activity, has been reported by Schubert et al.
The polymers were obtained by thiol–ene photoaddition of a tertiary amine-containing thiol onto an alkene-containing precursor copoly(2-oxazoline), followed by betainization with 1,3-propansultone and β-propiolactone. The polymers and their intermediates were characterized by means of 1H NMR spectroscopy and size exclusion chromatography. The influence of the zwitterionic polymers on the aggregation and hemolysis of erythrocytes, the whole blood viscosity, the platelet and complement activation as well as the blood coagulation has been studied in detail. In addition, the cytotoxicity of the materials has been evaluated.
It was found that the zwitterionic POx show no negative interactions with blood. Moreover, anticoagulant activity via the intrinsic and/or the common coagulation pathway was observed. The high hemocompatibility and the low cytotoxicity as well as the beneficial anticoagulant activity of the presented zwitterionic poly(2-oxazoline)s demonstrate their potential for the use in biomedical applications.
Zwitterionic poly(2-oxazoline)s as promising candidates for blood contacting applications by Lutz Tauhardt, David Pretzel, Kristian Kempe, Michael Gottschaldt, Dirk Pohlers and Ulrich S. Schubert Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 5751-5764.
Remzi Becer is a web-writer and advisory board member for Polymer Chemistry. He is currently a Senior Lecturer in Materials Science and the director of the Polymer Science and Nanotechnology masters programme at Queen Mary, University of London. Visit www.becergroup.com for more information!