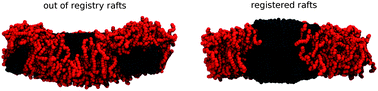Read here for free until Nov 11
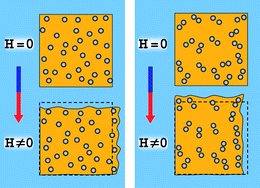
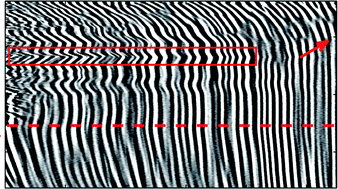
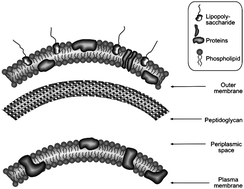
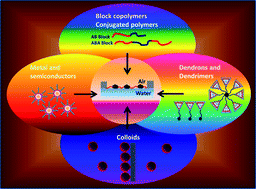 Langmuir monolayer, Langmuir-Blodgett and Langmuir-Schaefer film techniques are highly useful for determining equilibrium and dynamic behaviour in thin monolayers at air-water interfaces. Although the fabrication of ultrathin films has largely been supplanted by layer-by-layer assembly approaches, these techniques are still essential tools for studying new phenomenon in nanomaterials and in nanostructuring well-known or new materials for phenomenological observation and device fabrication. This review highlights the investigation of various amphiphilic and non-amphilic nanomaterials utilizing these interfacial techniques.
Langmuir monolayer, Langmuir-Blodgett and Langmuir-Schaefer film techniques are highly useful for determining equilibrium and dynamic behaviour in thin monolayers at air-water interfaces. Although the fabrication of ultrathin films has largely been supplanted by layer-by-layer assembly approaches, these techniques are still essential tools for studying new phenomenon in nanomaterials and in nanostructuring well-known or new materials for phenomenological observation and device fabrication. This review highlights the investigation of various amphiphilic and non-amphilic nanomaterials utilizing these interfacial techniques.
To keep up-to-date with all the latest research, sign up for the Soft Matter e-Alert or RSS feeds or follow Soft Matter on Twitter or Facebook.