Read these Hot Articles for free until 8 Sept >>>
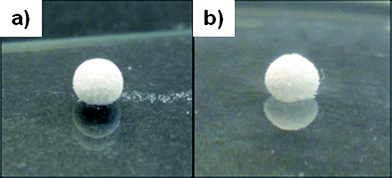
Liquid Marbles are stabilised on the surface of an acidic liquid due to hydrophobic components. However, once the pH reaches 5.5 the stabilising chains become to hydrophilic and the sphere collapses. The organic polymer particles were made-up of polyacid-stabilised polystyrene latex. Damien Dupin, Kate L. Thompson and Steven P. Armes, Soft Matter, 2011, 7, 6797-6800,DOI: 10.1039/C1SM05889D
‘Liquid marble’ deposited onto (a) a glass slide and (b) the surface of liquid water in a Petri dish.
Partially fluorinated amphiphiles and their interaction with biomembrane lipids in Langmuir monolayers is studied in this Hot Article. This provides fundamental insights into the molecular function of biomembrane components and support for the biomedical use of fluorinated materials. Shorter perfluoroalkyl chains may have more potential for clinical use than higher fluorinated chains. Hiromichi Nakahara, Marie Pierre Krafft, Akira Shibata and Osamu Shibata, Soft Matter, 2011, 7, 7325-7333, DOI: 10.1039/C1SM05647F
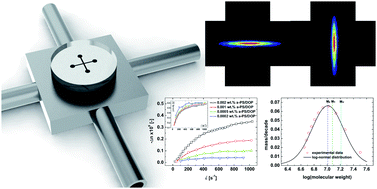
Cross-slot extensional flow oscillatory rheometry, an opto-microfluidic technique, is used to quantify the response of elastic fluids to extensional flows. This understanding is necessary for optimising fluid composition for technological applications such as ink-jet printing. Elastic fluids are complex fluids which respond to applied stress with a combination of solid-like elasticity and liquid-like ability to flow. Simon J. Haward, Vivek Sharma and Jeffrey A. Odell, Soft Matter, 2011, DOI: 10.1039/C1SM05493G