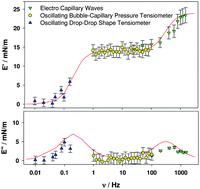
Polymer composites with smart optical properties
Andrea Pucci, Ranieri Bizzarri and Giacomo Ruggeri, Soft Matter, 2011, 7, 3689-3700
DOI: 10.1039/C0SM01038C
Stimulus responsive nanogels for drug delivery
Liusheng Zha, Brittany Banik and Frank Alexis, Soft Matter, 2011, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C0SM01307B
Suppressing the coffee stain effect: how to control colloidal self-assembly in evaporating drops using electrowetting
H. B. Eral, D. Mampallil Augustine, M. H. G. Duits and F. Mugele, Soft Matter, 2011, 7, 4954-4958
DOI: 10.1039/C1SM05183K
Morphology of polymer-based bulk heterojunction films for organic photovoltaics
Matthias A. Ruderer and Peter Müller-Buschbaum, Soft Matter, 2011, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C0SM01502D
Cubic crystals from cubic colloids
Laura Rossi, Stefano Sacanna, William T. M. Irvine, Paul M. Chaikin, David J. Pine and Albert P. Philipse, Soft Matter, 2011, 7, 4139-4142
DOI: 10.1039/C0SM01246G
Janus interface materials: superhydrophobic air/solid interface and superoleophobic water/solid interface inspired by a lotus leaf
Qunfeng Cheng, Mingzhu Li, Yongmei Zheng, Bin Su, Shutao Wang and Lei Jiang, Soft Matter, 2011, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C1SM05452J
Stimulus responsive core-shell nanoparticles: synthesis and applications of polymer based aqueous systems
Olivier J. Cayre, Nelly Chagneux and Simon Biggs, Soft Matter, 2011, 7, 2211-2234
DOI: 10.1039/C0SM01072C
Liquid marbles: principles and applications
Glen McHale and Michael I. Newton, Soft Matter, 2011, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C1SM05066D
Self-assembled aggregates of dendritic-linear copolymers: vesicles and microspheres
Jiwen Wu, Hui Tang and Peiyi Wu, Soft Matter, 2011, 7, 4166-416
DOI: 10.1039/C1SM05085K










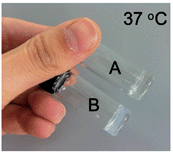

 Showcasing work from the University of Basel, Switzerland, in collaboration with the University of Antwerp, Belgium-
Showcasing work from the University of Basel, Switzerland, in collaboration with the University of Antwerp, Belgium-