The following HOT articles have been highlighted by the reviewers of the articles as being particularly interesting or significant pieces of research. These are all free to access until 30/09/2015. The order they appear in the list has no meaning or ranking.
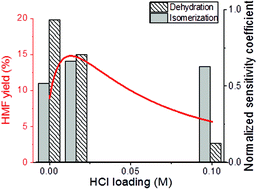
Tandem Lewis/Brønsted homogeneous acid catalysis: conversion of glucose to 5-hydoxymethylfurfural in an aqueous chromium(III) chloride and hydrochloric acid solution
T. Dallas Swift, Hannah Nguyen, Andrzej Anderko, Vladimiros Nikolakis and Dionisios G. Vlachos
Journal Article
DOI: 10.1039/C5GC01257K, Paper
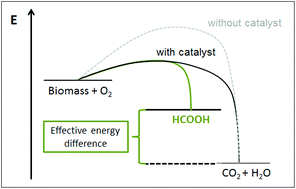
Expanding the scope of biogenic substrates for the selective production of formic acid from water-insoluble and wet waste biomass
Jakob Albert and Peter Wasserscheid
Journal Article
DOI: 10.1039/C5GC01474C, Paper
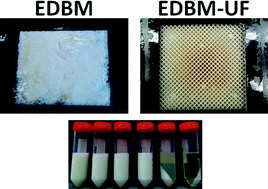
Hybrid bipolar membrane electrodialysis/ultrafiltration technology assisted by a pulsed electric field for casein production
Sergey Mikhaylin, Victor Nikonenko, Gérald Pourcelly and Laurent Bazinet
Journal Article
DOI: 10.1039/C5GC00970G, Paper
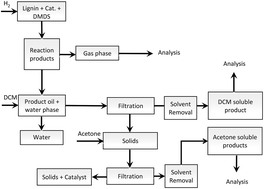
Solvent free depolymerization of Kraft lignin to alkyl-phenolics using supported NiMo and CoMo catalysts
Chowdari Ramesh Kumar, Narani Anand, Arjan Kloekhorst, Catia Cannilla, Giuseppe Bonura, Francesco Frusteri, Katalin Barta and Hero Jan Heeres
Journal Article
DOI: 10.1039/C5GC01641J, Paper
From themed collection Lignin chemistry and valorisation
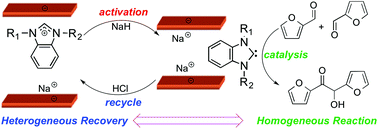
An interchangeable homogeneous ⇔ heterogeneous catalyst system for furfural upgrading
Lu Wang and Eugene Y.-X. Chen
Journal Article
DOI: 10.1039/C5GC01648G, Communication






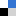










 High purity silicon is essential for manufacturing solar panels. Unfortunately this prerequisite conversion of silica to elemental silicon requires a lot of energy, and the associated greenhouse gas emissions are significant. It has now been demonstrated that the ashes from burning biomass (rice hulls in this case) can provide a rich source of silica than can be reduced to give solar grade silicon.
High purity silicon is essential for manufacturing solar panels. Unfortunately this prerequisite conversion of silica to elemental silicon requires a lot of energy, and the associated greenhouse gas emissions are significant. It has now been demonstrated that the ashes from burning biomass (rice hulls in this case) can provide a rich source of silica than can be reduced to give solar grade silicon.