On Thursday the 27th September, Professor James Clark from the University of York, UK, gave a public lecture at The Chemistry Centre in London on “From Waste to Wealth using Green Chemistry“.
The world today faces the fundamental issues of increasing waste but decreasing resources as it tries to cope with the ever increasing consumption of a growing population. Many of the raw resources and elements needed for the manufacture of important products used everyday are now running out. For example, in our search for ‘carbon-free’ products we have then created additional problems by significantly depleting the world’s resource of other elements, such as germanium.  We generate so much waste, but what do we do with it? How can we deal with our waste more efficiently?
We generate so much waste, but what do we do with it? How can we deal with our waste more efficiently?
The only way these problems can be met and dealt with is through a fundamentally different approach to the way we consume resources. Professor Clark’s lecture shows how by considering our waste as an opportunity rather than a problem, we can fully move towards a truly sustainable resource consumption model and give our children some hope for the future.
The event, sponsored by GlaxoSmithKline, was strongly attended by an audience of 100 people from a broad range of different backgrounds. The event generated lots of questions and some lively debates which continued long after the lecture had ended.
Missed the lecture? You can watch Professor Clark’s lecture in full on The Reaction website!
Professor Clark is the founding Editor of Green Chemistry and is also one of the Editors of the RSC Green Chemistry Book Series – find out more here.
You may also be interested in a few of Professor Clark’s recent Green Chemistry articles – free to access until the 9th November 2012:
Preparation and characterisation of bioplastics made from cottonseed protein, H.-B. Yue, Y.-D. Cui, P. S. Shuttleworth and James H. Clark, Green Chem., 2012, 14, 2009-2016
Thermosetting resin based on epoxidised linseed oil and bio-derived crosslinker, Nontipa Supanchaiyamat, Peter S. Shuttleworth, Andrew J. Hunt, James H. Clark and Avtar S. Matharu, Green Chem., 2012, 14, 1759-1765
A quantitative comparison between conventional and bio-derived solvents from citrus waste in esterification and amidation kinetic studies, James H. Clark, Duncan J. Macquarrie and James Sherwood, Green Chem., 2012, 14, 90-93
Switchable adhesives for carpet tiles: a major breakthrough in sustainable flooring, Peter S. Shuttleworth, James H. Clark, Robert Mantle and Nigel Stansfield, Green Chem., 2010, 12, 798-803
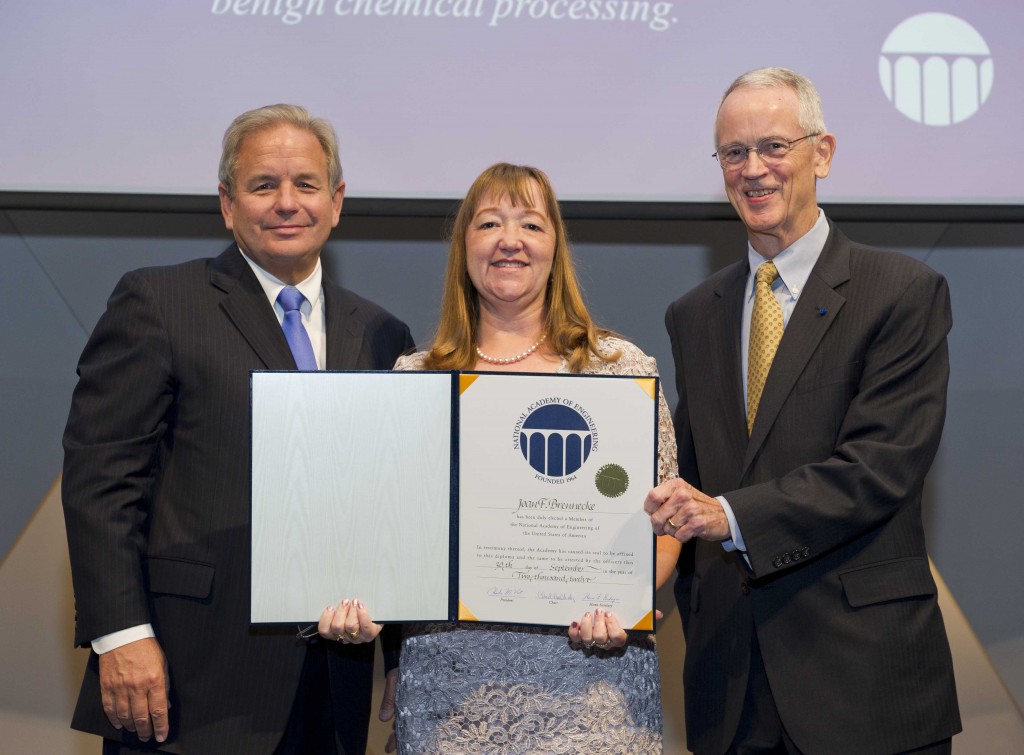 Green Chemistry Advisory Board member Joan Brennecke, the Keating-Crawford Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at the University of Notre Dame, USA, has been elected a member of the National Academy of Engineering. This honour has been awarded “for innovation in the use of ionic liquids and supercritical fluids for environmentally benign chemical processing.”
Green Chemistry Advisory Board member Joan Brennecke, the Keating-Crawford Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at the University of Notre Dame, USA, has been elected a member of the National Academy of Engineering. This honour has been awarded “for innovation in the use of ionic liquids and supercritical fluids for environmentally benign chemical processing.” 














 Professor
Professor 



