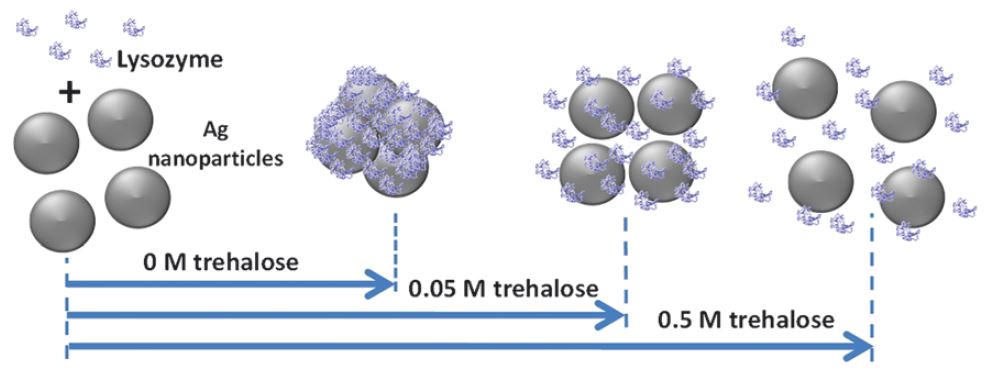
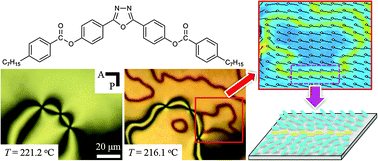
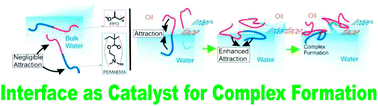
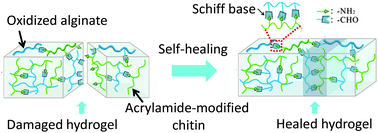
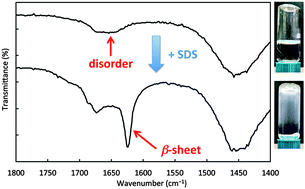
The interaction of proteins with nanoparticles has significant applications for clinical and biomedical therapies, specifically the field of theranostics, where diagnostic and therapeutic agents are combined into a single entity. Unfortunately, it has been well documented that attachment of proteins to nanoparticle surfaces leads to deformation of the protein and loss of protein activity. Aggregates of proteins form on the particle and induce aggregate formation of the particles themselves, hindering any theranostic capability.
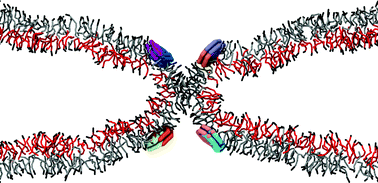
In a recent communication in Soft Matter, researchers from Johns Hopkins University, USA, and Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, India, describe a simple chemical method for solving this dilemma; addition of sugar. The naturally occurring disaccharide, trehalose, has demonstrated the ability to stabilize protein structures and shield them from thermal stress and dehydration. The protective nature of trehalose has been described by three hypotheses: (1) mechanical entrapment of the protein within the sugar molecules, (2) hydrogen bonding of the trehalose with the protein for chemical stabilization, (3) or water entrapment between the surface of the protein and trehalose. The research team exploited the protective properties of trehalose to insulate the protein, lysozyme, while the protein was exposed to silver nanoparticles, thus preventing denaturing of the protein.
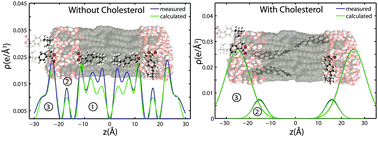
Without chemical stabilization, lysozyme aggregated on the nanoparticle surface and had significant structural deorganization. In the presence of trehalose, lysozyme maintained its active conformation and exhibited limited or no aggregation. By adjusting the concentration of trehalose in solution, nanoparticle-protein interactions were modulated. Analytical methods, including UV-vis absorbance, circular dichroism, and surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) illustrated and characterized the changes is binding of the lysozyme to the silver nanoparticle surface and the enhanced stability of the protein. The proof-of-concept system created a biocompatible environment for nanoparticles and proteins to engage without compromising lysozyme structure or activity. The proposed method will facilitate the development of nanoparticle theranostics and opens new avenues for nanomedicine design.
See the full Soft Matter article here:
Revealing the trehalose mediated inhibition of protein aggregation through lysozyme-silver nanoparticle interaction
Soumik Siddhanta, Ishan Barman, and Chandrabhas Narayana
Soft Matter, 2015, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C5SM01896J
 Dr. Morgan M. Stanton is currently a postdoctoral researcher at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems in Stuttgart, Germany. She completed her Ph.D. in Chemistry from Worcester Polytechnic Institute in 2014. Read more about Morgan’s research publications here.
Dr. Morgan M. Stanton is currently a postdoctoral researcher at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems in Stuttgart, Germany. She completed her Ph.D. in Chemistry from Worcester Polytechnic Institute in 2014. Read more about Morgan’s research publications here.
Follow the latest Soft Matter publications and updates on Twitter @softmatter or on Facebook