Read these Hot Articles for free until June 22:
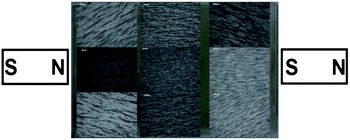
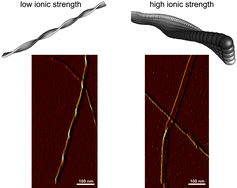
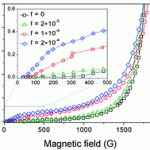
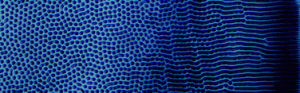
Magnetic flux lines were accurately modelled and mapped out in a new study on the effect of applied external fields to magnetic nanoparticle assembly. Ferrimagnetic iron oxide particles were used in the fossilized liquid assembly method, and agglomeration and sedimentation of the magnetic nanoparticles were also investigated . Ryan Schmidt, Jason Benkoski, Kevin Cavicchi and Alamgir Karim, Soft Matter, 2011, DOI: 10.1039/C1SM05057E
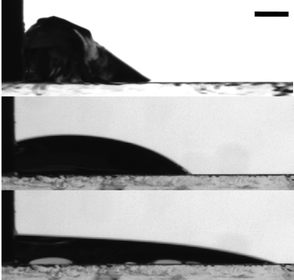
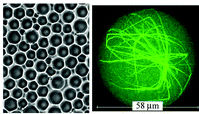
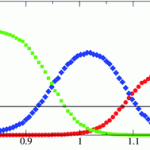
 Questions regarding heterogeneous nucleation in colloidal model systems are answered in this recent study. Although classical theories exist for crystal growth, the actual experimental determination of this process is still a challenge. Heterogeneous and homogeneous nucleation rate densities were both determined and compared. Andreas Engelbrecht, Rafaella Meneses and Hans Joachim Schöpe, Soft Matter, 2011, Advance Article, DOI: 10.1039/C1SM05246B
Questions regarding heterogeneous nucleation in colloidal model systems are answered in this recent study. Although classical theories exist for crystal growth, the actual experimental determination of this process is still a challenge. Heterogeneous and homogeneous nucleation rate densities were both determined and compared. Andreas Engelbrecht, Rafaella Meneses and Hans Joachim Schöpe, Soft Matter, 2011, Advance Article, DOI: 10.1039/C1SM05246B
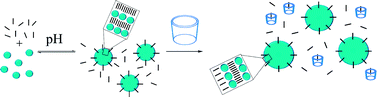
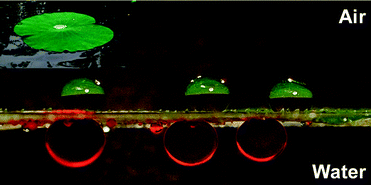
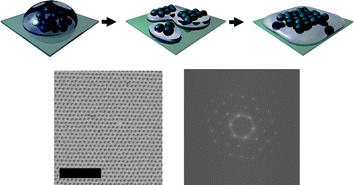
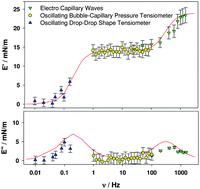 New investigations into interfacial properties of surfactant-decorated particles in interfacial layers have been performed. Nanometric dispersions of colloidal silica nanoparticles with a cationic surfactant, CTAB were studied, and surfactant rheology was studied on a broad frequency window for the first time. L. Liggieri, E. Santini, E. Guzmán, A. Maestro and F. Ravera, Soft Matter, 2011, Advance Article, DOI: 10.1039/C1SM05257H
New investigations into interfacial properties of surfactant-decorated particles in interfacial layers have been performed. Nanometric dispersions of colloidal silica nanoparticles with a cationic surfactant, CTAB were studied, and surfactant rheology was studied on a broad frequency window for the first time. L. Liggieri, E. Santini, E. Guzmán, A. Maestro and F. Ravera, Soft Matter, 2011, Advance Article, DOI: 10.1039/C1SM05257H