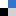Read free until 23 September>>>
 Antimicrobial and antiviral hydrogels: This brief review provides some illustrative examples of different types of antimicrobial (antibacterial/antifungal) and antiviral hydrogels. The triggered response of the hydrogels is discussed and a focus is placed on formulation principles, and on how the physicochemical properties of such hydrogels influence their antimicrobial/antiviral action. Martin Malmsten, Soft Matter, 2011, DOI: 10.1039/C1SM05809F
Antimicrobial and antiviral hydrogels: This brief review provides some illustrative examples of different types of antimicrobial (antibacterial/antifungal) and antiviral hydrogels. The triggered response of the hydrogels is discussed and a focus is placed on formulation principles, and on how the physicochemical properties of such hydrogels influence their antimicrobial/antiviral action. Martin Malmsten, Soft Matter, 2011, DOI: 10.1039/C1SM05809F
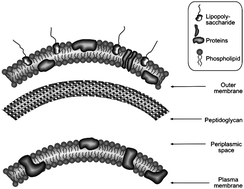
 Thermal liquid crystal phases: An interaction assisted approach for realization of biaxiality in smectic A phases is demonstrated in addition to the effectiveness of perfluoroarene-arene and C-H/F interactions as the intermolecular interactions. The slow rotation of the molecules showed unique phenomena such as no clear odd–even effect in their clearing and melting points. Keiki Kishikawa, Takahiro Inoue, Yoshiyuki Sasaki, Sumihiro Aikyo, Masahiro Takahashi and Shigeo Kohmoto, Soft Matter, 2011, 7, 7532-7538, DOI: 10.1039/C1SM05887H
Thermal liquid crystal phases: An interaction assisted approach for realization of biaxiality in smectic A phases is demonstrated in addition to the effectiveness of perfluoroarene-arene and C-H/F interactions as the intermolecular interactions. The slow rotation of the molecules showed unique phenomena such as no clear odd–even effect in their clearing and melting points. Keiki Kishikawa, Takahiro Inoue, Yoshiyuki Sasaki, Sumihiro Aikyo, Masahiro Takahashi and Shigeo Kohmoto, Soft Matter, 2011, 7, 7532-7538, DOI: 10.1039/C1SM05887H
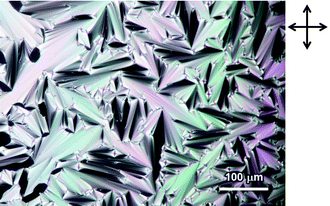
 Stimuli-responsive hydrogels: Researchers have functionalised poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gel with spirobenzopyrans and evaluated the effects of spontaneous ring-opening rates of the photo-chromic molecules on the light-responsive volume change of the subsequent gels. Rates of reswelling from the light-induced shrunken state of the spirobenzopyran-functionalized gels increased with increasing ring-opening rates of spirobenzopyrans in the gels. Taku Satoh, Kimio Sumaru, Toshiyuki Takagi and Toshiyuki Kanamori, Soft Matter, 2011, DOI: 10.1039/C1SM05797A
Stimuli-responsive hydrogels: Researchers have functionalised poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gel with spirobenzopyrans and evaluated the effects of spontaneous ring-opening rates of the photo-chromic molecules on the light-responsive volume change of the subsequent gels. Rates of reswelling from the light-induced shrunken state of the spirobenzopyran-functionalized gels increased with increasing ring-opening rates of spirobenzopyrans in the gels. Taku Satoh, Kimio Sumaru, Toshiyuki Takagi and Toshiyuki Kanamori, Soft Matter, 2011, DOI: 10.1039/C1SM05797A