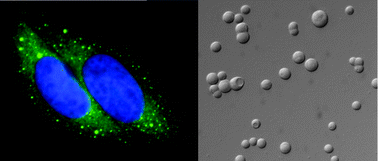
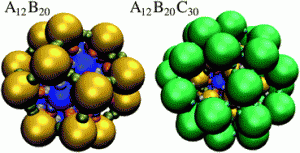Dr Brangwynne writes on the growing interest in intracellular protein bodies and their non-equilibrium, “active” behaviour in living cells. These bodies are non-membrane-bound organelles, such as Cajal bodies, the nucleolus and centrosomes which localise specific macromolecules (for example, RNA and protein). Their functions can include ribosome biogenesis, RNA splicing and cell division.
Archive for March, 2011
Hot Article: Designing foods that inhibit fat absorption
Emulsion-based foods are structured to improve taste, but how do these emulsions affect fat metabolism in the digestive system? The affect of structure on lipolysis in vitro, and triglyceride absorption in vivo, was investigated and researchers found lipid absorption was governed by emulsion instability.
Further studies on the physiological effects of food structure on lipid metabolism are underway.
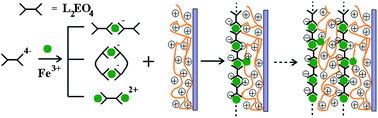
Hot Article: Functional metallopolyelectrolyte films
Fabrication of metal-ion containing layer-by-layer (LBL) assemblies has been simplified in a recently published procedure. Metallopolyelectrolytes were used to synthesise the LBL films, without the need for strict control of metal to ligand ratio, or preparation of coordination polymers. Through this synthesis fluorescent supermolecular thin films with desired colours were also fabricated.
Read the article for free here until April 8:
Yuru Lan, Limin Xu, Yun Yan, Jianbin Huang, Arie de Keizer, Nicolaas A. M. Besseling and Martien A. Cohen Stuart, Soft Matter, 2011, (Advance Article), DOI: 10.1039/C0SM01316A, Paper.
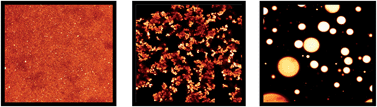
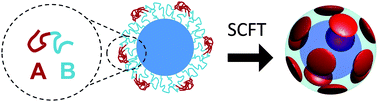
Hot Article: New algorithm for describing polymers in 3D spheres
The theory behind diblock-copolymer films grafted on spherical objects is investigated. An efficient numerical self-consistent field theory (SCFT) algorithm, combining spherical harmonics and the Crank-Nicolsen method, was developed. This algorithm could potentially be used for a wide range of spherical systems.
Read the article for free here until April 8!
Bart Vorselaars, Jaeup U. Kim, Tanya L. Chantawansri, Glenn H. Fredrickson and Mark W. Matsen
Soft Matter, 2011, (Advance Article), DOI: 10.1039/C0SM01242D, Paper
Is food the way forward?
When someone asks you about food, the first things that come to mind are taste, smell, texture and appearance, but not perhaps science. However, over recent years a number of popular science and cookery books have started to appear, highlighting how physics and chemistry are important when we cook. Indeed a number of chefs have even started to exploit science, conducting unusual culinary experiments, to create gastronomical delights.
For the academic year 2010/2011, Harvard University introduced a new course for their first year undergraduates “Science and cooking – from haute cuisine to the science of soft matter”. Lectures, conducted by internationally renowned Chefs and faculty, used food and cooking to introduce undergraduates to fundamental principles in applied physics and engineering. Titles of the lectures included “Heat, temperature and chocolate”, “Emulsions: Concepts and stabilising oil and water” and “Olive oil and viscosity”. In an interview with Physicsworld, David Weitz discussed one lecture where Joan Roca (El Celler de Can Roca) made a ‘super cool’ dessert. Joan distilled water with eucalyptus to make a very pure water. This was placed into a refrigerator and cooled it to -5C. On removal from the fridge, the water was still liquid. The liquid was then poured onto a dessert Joan was making. As soon as it hit the dessert, it froze. The dessert was supercooled as well as being ‘super cool’. This led naturally to a discussion on supercooling.
For those in the Soft Matter community, science and food is not a new concept. Understanding soft matter from colloids, to gels, to foams and emulsions and how it behaves are important in the structure, stability, taste, flavour and nutrition of food. A quick search of ‘food’ brings up over two hundred articles in Soft Matter alone, including a food science web theme issue. A few recent articles are highlighted below.
Understandably, the course at Harvard was particularly popular with the students, as well as the chefs – who also learnt a lot about what goes on when they cook. What is perhaps particularly interesting, from David Weitz’s comments on the course, is that not only did students give a round of applause when a new culinary dish was created, but also when a new equation was introduced. While inviting international chefs to give lectures is not possible for every scientific institution, taking an everyday topic like food might perhaps be the pathway to inspire and promote science in those both young and old.
Designer colloids – towards healthy everyday foods?
In this review paper (doi:10.1039/c001018a), Norton and Norton discuss the design and construction of colloids to encapsulate and release micronutrients. The aim is to create foods with reduced calorific content that look, taste and smell good. To reduced calorific content, pure fat can be replaced by an emulsion with the water phase containing very few calories. If this is designed in the correct way, such that the water is not released until the food reaches the stomach, then the consumer will not detect the water at all. A number of examples are given as to how this may be achieved using colloids, gels, Pickering emulsions and duplex emulsions. By careful design of the system, it is possible to add water to levels regarded as impossible e.g. 50% or more in chocolate. However, it is important that the whole process from eating to digestion is considered in the design of the emulsions and colloids. For example, when stabilised by emulsifiers that are not broken down by the stomach, emulsions stay intact. This means that the body is unaware of the content of fat in the food and can result in the consumer over eating. A recent study (highlighted in Chemistry World) has shown that the size of the fat droplet produced by the emulsion in the stomach is also important. Larger droplets take longer to digest and leave us feeling fuller for longer (doi:10.1039/C0SM01227K).
Nanoemulsions can also be utilised to encapsulate and deliver lipophilic components such as vitamins and drugs (doi:10.1039/c0sm00549e). In this tutorial review, McClements provides an overview of the current status in nanoemulsion research, from fabrication and properties to their applications and suitability for food products. Nanoemulsions are an exciting development over conventional emulsions, as they can be incorporated into transparent foods and beverages without changing the appearance of the product and have improved stability. However, wide spread use will not happen until suitable food-grade materials are identified and safety concerns overcome.
Three Hot Articles: Multicore micelles, hybrid organogels and patchy particles
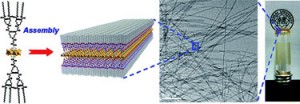 Polyoxometalate cluster-contained hybrid gelator and hybrid organogel: a new concept of softenization of polyoxometalate clusters. A team from Germany and China designed gelators to form hybrid organogels made of self-assembled hybrid nano-ribbons. The gelator is made of polyoxometalate cluster-contained hybrid molecules with two dendritic poly(urethane amide) wings. The team claim that these results could lead to new POM-containing functional materials. Soft Matter, 2011, DOI:10.1039/C1SM05032J Advance Article.
Polyoxometalate cluster-contained hybrid gelator and hybrid organogel: a new concept of softenization of polyoxometalate clusters. A team from Germany and China designed gelators to form hybrid organogels made of self-assembled hybrid nano-ribbons. The gelator is made of polyoxometalate cluster-contained hybrid molecules with two dendritic poly(urethane amide) wings. The team claim that these results could lead to new POM-containing functional materials. Soft Matter, 2011, DOI:10.1039/C1SM05032J Advance Article.
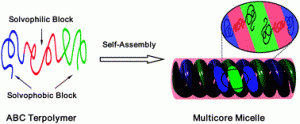 Discovering multicore micelles: insights into the self-assembly of linear ABC terpolymers in midblock-selective solvents. Linear ABC terpolymers with solvophobic–solvophilic–solvophobic block sequences are capable of self-assembling into multicore micelles. The team from East China University of Science and Technology used self-consistent field calculations to show that multicore micelles, such as the double-stranded superhelix, could be formed form the solution-state self-assembly of linear ABC terpolymers. These results expand the knowledge of the hierarchical assembly of copolymers and provide useful information for mimicking complex biological systems the team claim. Soft Matter, 2011, DOI:10.1039/C0SM01079K Advance Article
Discovering multicore micelles: insights into the self-assembly of linear ABC terpolymers in midblock-selective solvents. Linear ABC terpolymers with solvophobic–solvophilic–solvophobic block sequences are capable of self-assembling into multicore micelles. The team from East China University of Science and Technology used self-consistent field calculations to show that multicore micelles, such as the double-stranded superhelix, could be formed form the solution-state self-assembly of linear ABC terpolymers. These results expand the knowledge of the hierarchical assembly of copolymers and provide useful information for mimicking complex biological systems the team claim. Soft Matter, 2011, DOI:10.1039/C0SM01079K Advance Article
Templated self-assembly of patchy particles. Scientists at the University of Oxford have used computer simulations to explore templated self-assembly of complex target structures made from patchy particles. This assembly pathway allows dodecahedral shells to form readily, whereas these structures didn’t form in the absence of the template. The team suggest that DNA-mediated interactions could provide a potential route to achieve the required specificity in the patch-patch interactions for synthetic systems. Soft Matter, 2011, DOI:10.1039/C0SM01377C Advance Article
These articles are free to access until the 30th March (registration required)