Aromatic and aliphatic ketones reacted with aniline and molecular hydrogen in the presence of an easily available copper catalyst to give amines in high yields.
Reductive amination is one of the most important and effective C-N bond forming reactions and provides a general practical way to access amines. The reaction commonly involves chemicals which act hydrogen donors to be present, such as silanes and formates. 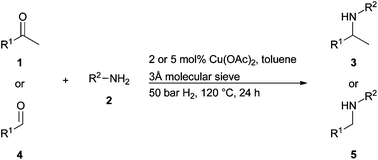
Here, Matthias Beller and colleagues from the Leibniz-Institute for Catalysis in Rostock, Germany report that simple Cu(OAc)2, an inexpensive and easily available catalyst, could catalyse the reductive amination of a variety of ketones with anilines and molecular hydrogen. The procedure does not require any complicated ligands or additional acid or base and represents the first example of a catalytic approach using copper and molecular hydrogen for reductive aminations.
This article is free to access until the 24th August 2012! Click on the link below to find out more…
Copper-catalyzed reductive amination of aromatic and aliphatic ketones with anilines using environmental-friendly molecular hydrogen, Svenja Werkmeister, Kathrin Junge and Matthias Beller, Green Chem., 2012, DOI: 10.1039/C2GC35565E
Keep up-to-date with the latest content in Green Chemistry by registering for our free table of contents alerts.