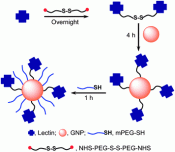
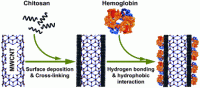
Because of their use in food producing animals, the risk of occurrence of unwanted residues in edible products exists.
Read this Critical Review on sample preparation methods for the determination of veterinary residues in food matrices by porous monolith microextraction-based techniques. Several porous monolith microextraction formats, including in-tube solid-phase extraction, stir bar sorptive extraction and stir rod sorptive extraction modes, are described. One referee commented that the review will be ‘a very useful guide for future study and application of correlative techniques.’
This is an important area of research as veterinary drugs are regularly administered via drinking water and feed with the aim of hindering the spread of disease amongst animals. However, even low levels of these drugs, including antibiotics and pesticides, can cause health issues in humans.
You can access the critical review for free until 28th June.
Methods of sample preparation for determination of veterinary residues in food matrices by porous monolith microextraction-based techniques
Fang Wei and Yu-Qi Feng
Anal. Methods, 2011
DOI: 10.1039/C1AY05079F
Why not take a look at another paper we’ve published this year on veterinary drug residue analysis
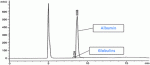
Development and validation (according to the 2002/657/EC regulation) of a method to quantify sulfonamides in porcine liver by fast partition at very low temperature and LC-MS/MS
Renata Pereira Lopes, Daniella Vasconcellos Augusti, Leonardo Francisco de Souza, Flávio Alves Santos, Josefa Abucater Lima, Eugênia Azevedo Vargas and Rodinei Augusti
Anal. Methods, 2011, 3, 606-613
DOI: 10.1039/C0AY00587H
And some from our sister journal, Analyst:
Semi-targeted residue screening in complex matrices with liquid chromatography coupled to high resolution mass spectrometry: current possibilities and limitations
Anton Kaufmann, Patrick Butcher, Kathryn Maden, Stephan Walker and Miryam Widmer
Analyst, 2011, 136, 1898-1909
DOI: 10.1039/C0AN00902D
Assessment of terahertz spectroscopy to detect antibiotic residues in food and feed matrices
Albert Redo-Sanchez, Gerard Salvatella, Regina Galceran, Eva Roldós, José-Antonio García-Reguero, Massimo Castellari and Javier Tejada
Analyst, 2011, 136, 1733-1738
DOI: 10.1039/C0AN01016B
High-throughput chemical residue analysis by fast extraction and dilution flow injection mass spectrometry
Sergio C. Nanita
Analyst, 2011, 136, 285-287
DOI: 10.1039/C0AN00720J