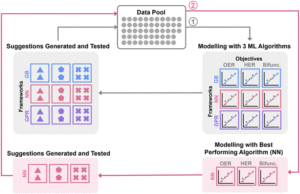
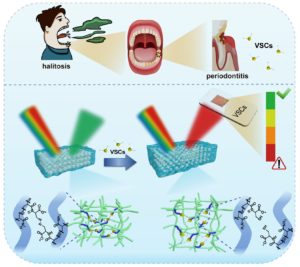
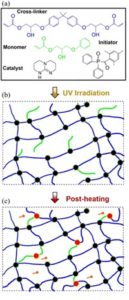
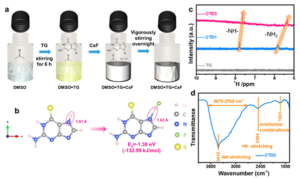
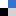For a considerable period, the engine of progress was fuelled primarily by economic incentives. However, this paradigm has shifted due to increased awareness of the environmental consequences of society. Focus has turned towards embracing sustainability as a precursor to assimilating the fruits of progress into industry. This trend leverages the conversion of different waste feedstock like plastics, metals, etc, into new added value matter. The added value matter could be fuels, solvents, organic substrates, new polymers, and functional materials.
Embracing the notion that “the new is often the well-forgotten old,” the use of biomass as a feedstock for materials with practicable qualities has been revisited and revitalized. The biomass is feedstock mainly derived from agricultural and forestry resources, and animal resources. Compared to other waste feedstock, such as plastic, electronic, and construction waste, biomass already fits more within the sustainable economic strategy due to its natural origin. The other side of this coin is the insufficient mechanical properties of biomass-derived materials which leads to poor durability and recyclability of functional materials from biomass.
Recent work from Leixiao Yu, Lingyan Gao, Shengyi Dong and team suggests a supramolecular strategy to overcome these limitations. They reported the conversion of 6 types of biomass (cellulose, guar gum, sericin protein, chitin, corn protein and potato starch) to functional materials via copolymerization with thioctic acid (TA) to afford poly[TA-biomass]. The material formation is driven by hydrogen bonding between TA and the polar functional groups in the biomass. Despite such non-covalent forces being reversible and inherently weaker than covalent bonds, prepared materials are proven to be highly impact resistant. The prepared poly[TA-biomass] is highly adhesive and water-resistant, however, it could be fully depolymerized by simple ethanol treatment and involved in the next cycle of polymerization-utilization without any obvious decay in mechanical strength. This anticipates potential applications of poly[TA-biomass as anti-water, impact resistant materials. The team expanded the potential application directions to the biomedical field by demonstrating high biocompatibility, nontoxicity, and antimicrobial effects towards both gram-positive and negative bacteria, attributed to TA. For instance, the newly prepared poly[TA-biomass] may hold promise for smart packaging or wound healing materials.
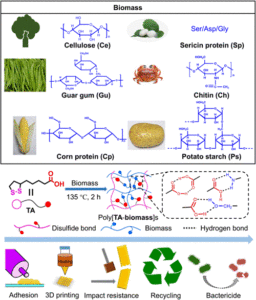
Figure 1:Chemical structures of biomass (upper block,) and preparation of poly[TA-biomass]s via supramolecular approach – formation of hydrogen bonding hydrogen bonding between thioctic and the polar functional groups in the biomass (middle block) and key advantages of poly[TA-biomass]s materials. Reproduced from DOI: 10.1039/d3mh01692g with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry.
To find out more, please read:
A supramolecular approach for converting renewable biomass into functional materials
Yunfei Zhang, Changyong Cai, Ke Xu, Xiao Yang, Leixiao Yu, Lingyan Gao and Shengyi Dong
Mater. Horiz., 2024, Advance Article, DOI: 10.1039/D3MH01692G
About the blogger

Dr Olga Guselnikova is a member of the Materials Horizons Community Board. She recently joined the Center for Electrochemistry and Surface Technology (Austria) to work on functional materials as a group leader. Dr. Guselnikova received her PhD degree in chemistry from the University of Chemistry and Technology Prague (Czech Republic) and Tomsk Polytechnic University (Russia) in 2019. Her research interests are related to surface chemistry for functional materials. This means that she is applying her background in organic chemistry to materials science: plasmonic and polymer surfaces are hybridized with organic molecules to create high-performance elements and devices.
|