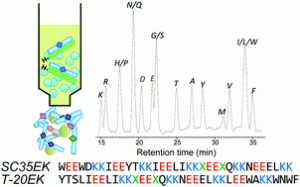
By Philippa Ross
Hollow silica nanoparticles filled with gas behave as efficient contrast agents for use in ultrasound imaging. This could improve detection of tumours in breast cancer patients, claim US scientists.
Ultrasound imaging is a safe, fast and non-invasive technique used for medical diagnosis. However, one shortcoming is the inferior image contrast compared to more sophisticated magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). To improve this, radiologists use microbubble contrast agents to enhance the reflection of ultrasonic waves and therefore improve the quality of the ultrasound image, or radioactive seeds that are injected into the patient before surgery to visualise the entire tumour.
However, the contrast particles – normally comprised of a soft protein outer shell and a gas core – can be unstable due to their high sensitivity to changes in pressure, while the radioactive seeds have to be painfully injected into the patient and only last a few hours.
Now, a team led by William Trogler at the Univeristy of Califonia, San Diego have developed a stable, hard shell, hollow particle which, when filled with gas, produces a ultrasound signal and can be safely and painlessly injected into breast tissue to locate tumours. The gas-filled microbubbles adhere to human breast tissue for days and have a longer imaging lifetime than their soft counterparts, explains Trogler. So if used in early stage breast cancer patients, they could help surgeons better visualise the tumours and remove it all in one procedure.
Elizabeth Shaughnessy, a specialist in breast diseases at the University of Cincinnati in the US agrees. ‘The injection of these silica hollow spheres with gas-filled contrast provides a less toxic alternative, [to radioactive seeds] that won’t degrade within a short time period.’ She adds that the work is ‘highly innovative and will have great appeal to surgeons, radiologists and patients, as well as operating staff.‘
It is still early days but next Trogler and his team hope to move to animal models, toxicology studies and eventually clinical trials. Methods are also being developed to make biodegradable gas filled silica micro and nanoshells that would broaden the possible imaging applications.
This story has been published on the Highlights in Chemical Biology website.
Read the paper free to access
Hard shell gas-filled contrast enhancement particles for colour Doppler ultrasound imaging of tumors
H. Paul Martinez, Yuko Kono, Sarah L. Blair, Sergio Sandoval, Jessica Wang-Rodriguez, Robert F. Mattrey, Andrew C. Kummel and William C. Trogler, Med. Chem. Commun., 2010, 1, 266
DOI: 10.1039/c0md00139b














 Mark Bunnage is executive director of worldwide medicinal chemistry at Pfizer in Sandwich, UK. His areas of responsibility include chemistry leadership for regenerative medicine. He is also a member of the Executive Committee of the European Federation for Medicinal Chemistry (EFMC) and an editorial board member for MedChemComm.
Mark Bunnage is executive director of worldwide medicinal chemistry at Pfizer in Sandwich, UK. His areas of responsibility include chemistry leadership for regenerative medicine. He is also a member of the Executive Committee of the European Federation for Medicinal Chemistry (EFMC) and an editorial board member for MedChemComm.