This month sees the following articles in Energy & Environmental Science that are in the top ten most accessed in March:
Uniform V2O5 nanosheet-assembled hollow microflowers with excellent lithium storage properties
An Qiang Pan, Hao Bin Wu, Lei Zhang and Xiong Wen (David) Lou
Energy Environ. Sci., 2013,6, 1476-1479
DOI: 10.1039/C3EE40260F
Graphene quantum dots: an emerging material for energy-related applications and beyond
Zhipan Zhang, Jing Zhang, Nan Chena and Liangti Qu
Energy Environ. Sci., 2012,5, 8869-8890
DOI: 10.1039/C2EE22982J
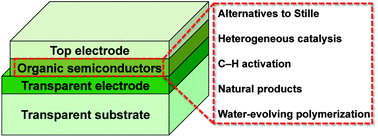
Graphene and its derivatives for the development of solar cells, photoelectrochemical, and photocatalytic applications
Da Chen, Hao Zhang, Yang Liua and Jinghong Li
Energy Environ. Sci., 2013,6, 1362-1387
DOI: 10.1039/C3EE23586F
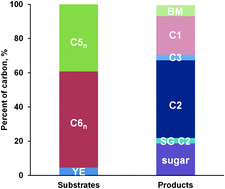
The role of biofuels in the future energy supply
Luis Caspeta, Nicolaas A. A. Buijs and Jens Nielsen
Energy Environ. Sci., 2013,6, 1077-1082
DOI: 10.1039/C3EE24403B
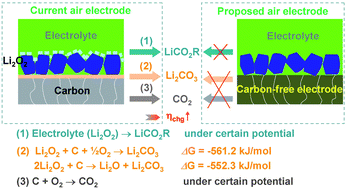
Lithium–oxygen batteries: bridging mechanistic understanding and battery performance
Yi-Chun Lu, Betar M. Gallant, David G. Kwabi, Jonathon R. Harding, Robert R. Mitchell, M. Stanley Whittingham and Yang Shao-Horn
Energy Environ. Sci., 2013,6, 750-768
DOI: 10.1039/C3EE23966G
A membrane-free lithium/polysulfide semi-liquid battery for large-scale energy storage
Yuan Yang, Guangyuan Zheng and Yi Cui
Energy Environ. Sci., 2013,6, 1552-1558
DOI: 10.1039/C3EE00072A
High performance hybrid solar cells sensitized by organolead halide perovskites
Bing Cai, Yedi Xing, Zhou Yang, Wen-Hua Zhang and Jieshan Qiu
Energy Environ. Sci., 2013,6, 1480-1485
DOI: 10.1039/C3EE40343B
Highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells: progress and future challenges
Shufang Zhang, Xudong Yang, Youhei Numata and Liyuan Han
Energy Environ. Sci., 2013,6, 1443-1464
DOI: 10.1039/C3EE24453A
Challenges in the development of advanced Li-ion batteries: a review
Vinodkumar Etacheri, Rotem Marom, Ran Elazari, Gregory Salitra and Doron Aurbach
Energy Environ. Sci., 2011,4, 3243-3262
DOI: 10.1039/C1EE01598B
Photoelectrochemical cells for solar hydrogen production: current state of promising photoelectrodes, methods to improve their properties, and outlook
Zhaosheng Li, Wenjun Luo, Minglong Zhang, Jianyong Fenga and Zhigang Zou
Energy Environ. Sci., 2013,6, 347-370
DOI: 10.1039/C2EE22618A
Why not take a look at the articles today and blog your thoughts and comments below
Fancy submitting an article to EES? Then why not submit to us today!
Comments Off on Top 10 most-read EES articles in March