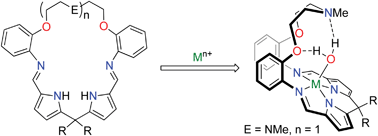
The catalytic potential of metal nanoparticles is widely understood and some are already used for heterogeneous catalysis. In a dedication to Professor Cole-Hamilton, Karine Philippot and Bruno Chaudret et al. report the synthesis and characterisation of uniquely stabilised RuPt nanoparticles.
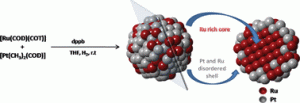 A diphenylphospine was used to stabilise bimetallic RuPt nanoparticles, both decorating them and affecting their chemical composition. Neither an ordered alloy nor a core-shell structure was produced; instead, as proven by scattering and spectroscopic techniques, very disordered nanoparticles with Ru cores and alloy shells were observed. The mechanism that produces such an “onion” structure is thought to involve the reaction of the diphosphine ligands with Ru at the beginning of the reaction.
A diphenylphospine was used to stabilise bimetallic RuPt nanoparticles, both decorating them and affecting their chemical composition. Neither an ordered alloy nor a core-shell structure was produced; instead, as proven by scattering and spectroscopic techniques, very disordered nanoparticles with Ru cores and alloy shells were observed. The mechanism that produces such an “onion” structure is thought to involve the reaction of the diphosphine ligands with Ru at the beginning of the reaction.
The use of reactive ligands in the synthesis of bimetallic nanoparticles can modify their structure, suggesting the possibility of finely tailoring the structure and surface of such nanoparticles in the future. These modifications have already shown promise, with CO poisoning of RuPt nanoparticles having much less of an effect on hydrogenation reactions than with analagous pure Ru examples.
To find out more about these new bimetallic nanoparticles, download this HOT article now.
On the influence of diphosphine ligands on the chemical order in small RuPt nanoparticles: combined structural and surface reactivity studies
Patricia Lara, Tuğçe Ayvalı, Marie-José Casanove, Pierre Lecante, Alvaro Mayoral, Pier-Francesco Fazzini, Karine Philippot and Bruno Chaudret