
Welcome to the 2024 HOT article round up!
This is our first full year for the 2024 RSC Mechanochemistry HOT Article Collection to showcase all of the articles selected by our reviewers and handling editors as HOT in 2024.
We hope you enjoy reading and as always, all of our articles are open access so you can easily share your favourites online and with your colleagues.
Explore the full collection!
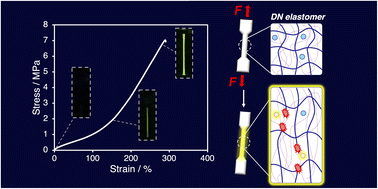
Visualization of mechanochemical polymer-chain scission in double-network elastomers using a radical-transfer-type fluorescent molecular probe
Takumi Yamamoto, Akira Takahashi and Hideyuki Otsuka
RSC Mechanochem., 2024,1, 63-68
DOI: 10.1039/D3MR00016H
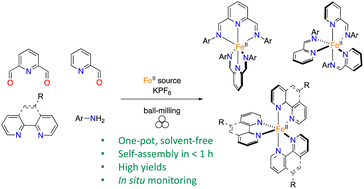
Ball-milling for efficient synthesis of pyridine-containing iron(ii) photosensitizers
Enita Rastoder, Thierry Michel, Frédéric Lamaty and Xavier Bantreil
RSC Mechanochem., 2024,1, 116-122
DOI: 10.1039/D3MR00033H
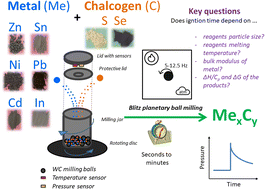
Mechanically induced self-propagating reactions (MSRs) to instantly prepare binary metal chalcogenides: assessing the influence of particle size, bulk modulus, reagents melting temperature difference and thermodynamic constants on the ignition time
Matej Baláž, Róbert Džunda, Radovan Bureš, Tibor Sopčák and Tamás Csanádi
RSC Mechanochem., 2024,1, 94-105
DOI: 10.1039/D3MR00001J
Mechanochemical synthesis of zinc-doped hydroxyapatite for tunable micronutrient release
Mohamed Ammar, Ricardo Bortoletto-Santos, Caue Ribeiro, Lihua Zhang and Jonas Baltrusaitis
RSC Mechanochem., 2024,1, 263-278
DOI: 10.1039/D3MR00012E

Revealing the mechanism of reductive, mechanochemical Li recycling from LiFePO4
David Geiß, Oleksandr Dolotko, Sylvio Indris, Christian Neemann, Andrei Bologa, Thomas Bergfeldt, Michael Knapp and Helmut Ehrenberg
RSC Mechanochem., 2024,1, 349-360
DOI: 10.1039/D4MR00014E

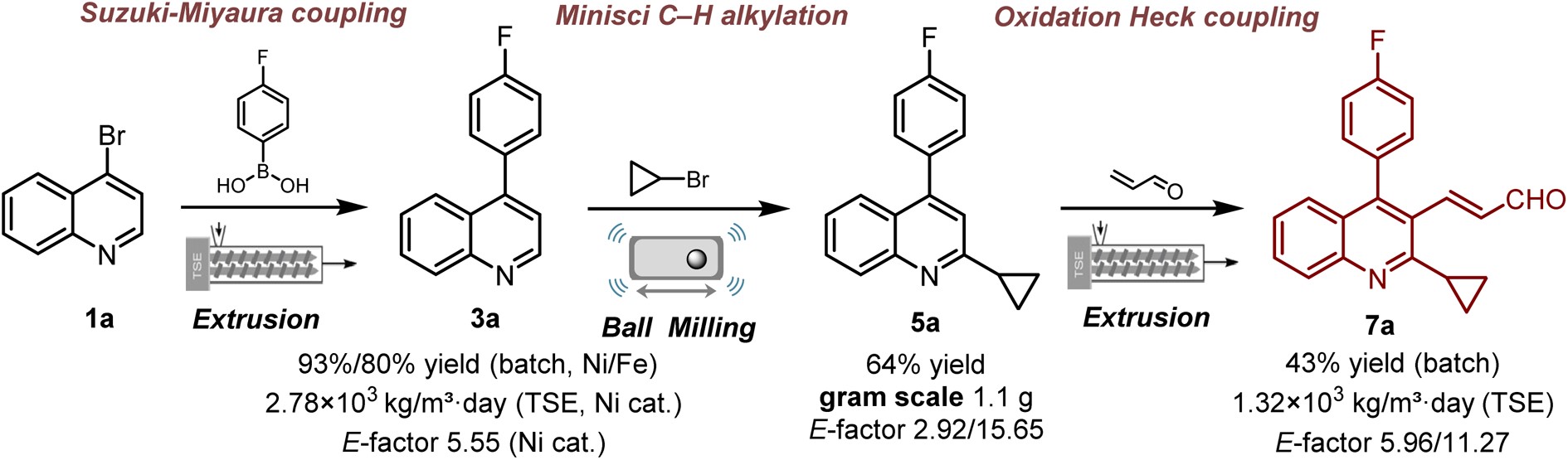
Total mechano-synthesis of 2-cyclopropyl-4-(4-fluorophenyl)quinoline-3-acrylaldehyde—a pivotal intermediate of pitavastatin
Jingbo Yu, Yanhua Zhang, Zehao Zheng and Weike Su
RSC Mechanochem., 2024,1, 367-374
DOI: 10.1039/D4MR00036F

Rapid and efficient mechanosynthesis of alkali and alkaline earth molybdates
Andres Lara-Contreras, Patrick Julien, Jennifer Scott and Emily C. Corcoran
RSC Mechanochem., 2024,1, 477-485
DOI: 10.1039/D4MR00042K
Submit to RSC Mechanochemistry today! Check out our author guidelines for information on our article types or find out more about the advantages of publishing in a Royal Society of Chemistry journal.
Keep up to date with our latest HOT articles, Reviews, Collections & more by joining our group on LinkedIn. You can also keep informed by signing up to our E-Alerts.









 In my field of soft matter mechanochemistry, we have seen some pretty exciting progress thanks to the development of increasing numbers of synthetic molecules that respond to mechanical force in specific ways. Some key examples are mechanochromic, mechanofluorescent and mechanoluminescent reporters, as well as force-triggered release mechanisms through mechanochemical linkers, reactions kick-started by radicals or mechanocatalysts, mechanochemical switches, and, more recently, artificial catch bonds. What is really exciting is that more and more of these mechanoresponsive systems are working in water, which opens up a lot of possibilities for integrating them with biological systems.
In my field of soft matter mechanochemistry, we have seen some pretty exciting progress thanks to the development of increasing numbers of synthetic molecules that respond to mechanical force in specific ways. Some key examples are mechanochromic, mechanofluorescent and mechanoluminescent reporters, as well as force-triggered release mechanisms through mechanochemical linkers, reactions kick-started by radicals or mechanocatalysts, mechanochemical switches, and, more recently, artificial catch bonds. What is really exciting is that more and more of these mechanoresponsive systems are working in water, which opens up a lot of possibilities for integrating them with biological systems. There is considerable evidence that mechanochemistry is often better than other synthetic methods, especially solution-based ones. Mechanochemistry uses mechanical force to drive chemical reactions, and it can be more efficient, resource-saving and environmentally friendly than traditional solutions.
There is considerable evidence that mechanochemistry is often better than other synthetic methods, especially solution-based ones. Mechanochemistry uses mechanical force to drive chemical reactions, and it can be more efficient, resource-saving and environmentally friendly than traditional solutions. Mechanochemistry has always been a paradigm-shifting method for conducting chemical reactions. While we often celebrate groundbreaking ideas in hindsight, they are not always embraced immediately. Consider Galileo Galilei, who faced life imprisonment for endorsing Copernicus’ theory that the Earth orbits the sun. Similarly, Alfred Wegener encountered not just skepticism, but outright hostility for proposing the concept of continental drift, suggesting that continents were once connected and moved across the Earth. One of Wegener’s detractors stated “It is certain the Wegener’s theory was established with a superficial use of scientific methods, ignoring the various fields of geology.” He continued to state “We can only try to keep our distance and beg him not to deal with geology any longer…” Even Einstein’s view of quantum physics was not all that favorable, famously stating “God does not play dice with the Universe” and describing what we now call quantum entanglement as “spooky action at a distance”. These examples highlight not just a mere clash of ideas, but also the hostility directed towards the individuals advocating them.
Mechanochemistry has always been a paradigm-shifting method for conducting chemical reactions. While we often celebrate groundbreaking ideas in hindsight, they are not always embraced immediately. Consider Galileo Galilei, who faced life imprisonment for endorsing Copernicus’ theory that the Earth orbits the sun. Similarly, Alfred Wegener encountered not just skepticism, but outright hostility for proposing the concept of continental drift, suggesting that continents were once connected and moved across the Earth. One of Wegener’s detractors stated “It is certain the Wegener’s theory was established with a superficial use of scientific methods, ignoring the various fields of geology.” He continued to state “We can only try to keep our distance and beg him not to deal with geology any longer…” Even Einstein’s view of quantum physics was not all that favorable, famously stating “God does not play dice with the Universe” and describing what we now call quantum entanglement as “spooky action at a distance”. These examples highlight not just a mere clash of ideas, but also the hostility directed towards the individuals advocating them. Mechanochemistry has the potential to revolutionise many industrial applications, such as energy, nanomaterials, and environmental remediation. By using mechanochemistry, our industry can potentially reduce their costs, waste, and environmental impact, while increasing their efficiency, quality, and innovation. Mechanochemistry can also enable the discovery of new compounds and mechanisms that are inaccessible by conventional methods.
Mechanochemistry has the potential to revolutionise many industrial applications, such as energy, nanomaterials, and environmental remediation. By using mechanochemistry, our industry can potentially reduce their costs, waste, and environmental impact, while increasing their efficiency, quality, and innovation. Mechanochemistry can also enable the discovery of new compounds and mechanisms that are inaccessible by conventional methods.