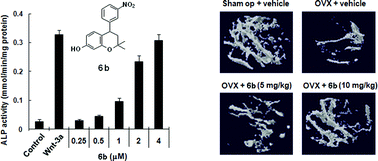
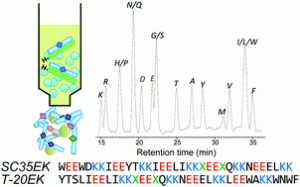
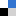Adam McCluskey and colleagues at The University of Newcastle have developed a library of compounds that can act as anti-cancer agents.
In this paper, they report the discovery of a family of 2-phenylacrylonitriles with excellent growth inhibition of a panel of ten human cancer cell lines.
Read this MedChemComm full paper free to access.
Library synthesis and cytotoxicity of a family of 2-phenylacrylonitriles and discovery of an estrogen dependent breast cancer lead compound
Mark Tarleton, Jayne Gilbert, Mark J. Robertson, Adam McCluskey and Jennette A. Sakoff
Med. Chem. Commun., 2011, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C0MD00147C , Concise Article