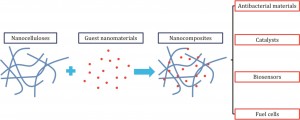
Nanocellulose (NC) provides a readily available and biodegradable substrate that can act as a novel template or carrier for a range of different nanomaterials (NMs) including carbonaceous, mineral and metal particles. NC is an ideal platform for inorganic NMs due to its high specific surface area, highly porous structure and high mechanical strength. The resulting NC combines the characteristics of both constituents therefore displaying synergistic properties useful for a variety of uses.
Peter Vikesland and colleagues from Virginia Tech and Duke University, USA provide a tutorial review discussing recent advances in the preparation of NC-based nanocomposites and their potential uses in addressing current and future environmental challenges. This is the first review of its kind to discuss the use of these novel nanocomposites in the context of environmental sciences and engineering applications.
You can download the full review for free* on our publishing platform
The authors describe:
- different forms in which NC is produced,
- how the NC can be derived both from plant materials and bacterial processes,
- how NC can be modified into a number of useful forms.
Furthermore, in-depth discussion of the different methods used in the preparation of NC and different types of composites is provided. This includes a discussion of how the guest NM can be incorporated in/on to the NC structure, guidance regarding the challenges faced in these processes and how researchers have address these problems, and instructions on the best available methods currently known for these procedures.
The review also details the uses of NC-based nanocomposities in key environmental science/engineering applications and summarises the practical considerations and advantages these provide over more conventional NMs. This focuses on four principal areas:
1) The better incorporation of antimicrobial materials such as Ag NMs into NC-based filters for air and drinking water purification.
2) The use of NC as a support for photocatalysts and metal catalysts used in the degradation of organic pollutants in water remediation.
3) The use of Au NP/NC biosensors for monitoring of water-borne pathogens and organic contaminants.
4) The use of NC-based nanocomposites in the design of superior energy conversion devices such as fuel cells, solar cells and Li-ion battery manufacturing.
Finally, potential directions of further research in the field of NC nanocomposites are highlighted. Specifically, researching methods to better control the size and distribution of NMs on or within the NC substrate, investigating how the loading of NMs influence the potential applications, and ways to prolong the lifetime and/or regenerate NMs to ensure their sustainability.
Cellulose is an abundant, cheap and renewable resource. Nanocellulose is shown to form useful nanocomposites with inorganic nanomaterials, which display valuable optical, catalytic, electrical properties. This review provides guidance to researchers in the field of environmental sciences and engineering on the production and uses for this type of nanocomposites to address current and emerging environmental challenges.
Environmental science and engineering applications of nanocellulose-based nanocomposites
Haoran Wei, Katia Rodriguez, Scott Renneckar and Peter J. Vikesland
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2014,1, 302
DOI: 10.1039/c4en00059e
* Access is free through a registered RSC account – click here to register