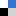Nanoparticles – they are really small; we can’t see them, hear them or feel them and therefore they are pretty hard to detect! Manuel David Montaño, from Colorado School of Mines, and colleagues have made improvements in the detection and characterization of engineered nanoparticles, simply by reducing the time of detection for each nanoparticle – the dwell time.
In order to determine the toxicity, fate and transport of nanoparticles in the environment, we first need to determine the size and quantity of nanoparticles in the environment. In order to determine the size and quantity of nanoparticles in the environment we need to be able to accurately detect these nanoparticles. Single particle ICP-MS (spICP-MS) is already a promising technique to detect and characterize low concentrations of engineered nanoparticles in biological and environmental matrices. Initially developed for aerosol particle analysis, spICP-MS uses time resolved analysis with dwell times of approximately 10miliseconds. So how does it work? A discrete pulse of intensity, origination from nanoparticle vaporization and ionization, can be detected – the signal generated by the ions can then be correlated to nanoparticle mass.
The problem – this method of detection only works on low concentrations of nanoparticles. In high concentrations of nanoparticles, two or more nanoparticles can be detected during the same dwell time giving invalid results. It appears that particles are larger in size and lower in concentration that they really would be in the environment. To overcome this problem, often samples have to be diluted considerably, making the results less environmentally relevant. In this study, instead of diluting the samples, researchers simply reduced the dwell time from milliseconds to microseconds. This improved the resolution and working range of spICP-MS, allowing a greater breadth of environmental samples to be analysed.
You can read the full paper for free* by clicking the link below
Improvements in the detection and characterization of engineered nanoparticles using spICP-MS with microsecond dwell times
M. D. Montaño, H. R. Badiei, S. Bazargan and J. F. Ranville
DOI: 10.1039/C4EN00058G
* Access is free through a registered RSC account – click here to register