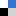Sean Lehman and Sarah Larsen from the University of Iowa review zeolite and mesoporous silica nanomaterials with emphasis on connections to the environment.
In recent years, there has been a great deal of interest in zeolites and mesoporous silica nanomaterials (MSNs). Zeolites are widely used in industry for applications such as catalysis, separations and gas adsorption, however the authors believe that these porous nanomaterials have a largely unrealized commercial potential for environmental applications.
This review article covers three major areas:
- Greener synthesis of zeolite and MSNs
- Potential of zeolite and MSNs for environmental applications
- The biological toxicity of zeolite and MSNs
Due to cost and reduced thermal stability MSNs are not as extensively applied as zeolite; however they are currently being investigated for potential environmental and biomedical applications. Their varied physiochemical properties open up a wide range of potential applications. The more applications that these porous nanomaterials have in industry, the greater the interested in developing greener synthesis for them and reducing their toxicity. With two measurements which are on the nanoscale, pore size as well as particle size, zeolites and MSN make very interesting nanomaterials.
This review describes both the environmental applications, including environmental catalysis and adsorption of environmental contaminants, and implications of zeolite and MSNs. Due to concerns that increased use of these materials translates to increased exposures, toxicity studies of both nanomaterials are also reviewed.
To read the full review for free* click the link below:
Zeolite and Mesoporous Silica Nanomaterials: Greener Syntheses, Environmental Applications and Biological Toxicity
Sean E Lehman and Sarah C Larsen
DOI: 10.1039/C4EN00031E, Critical Review
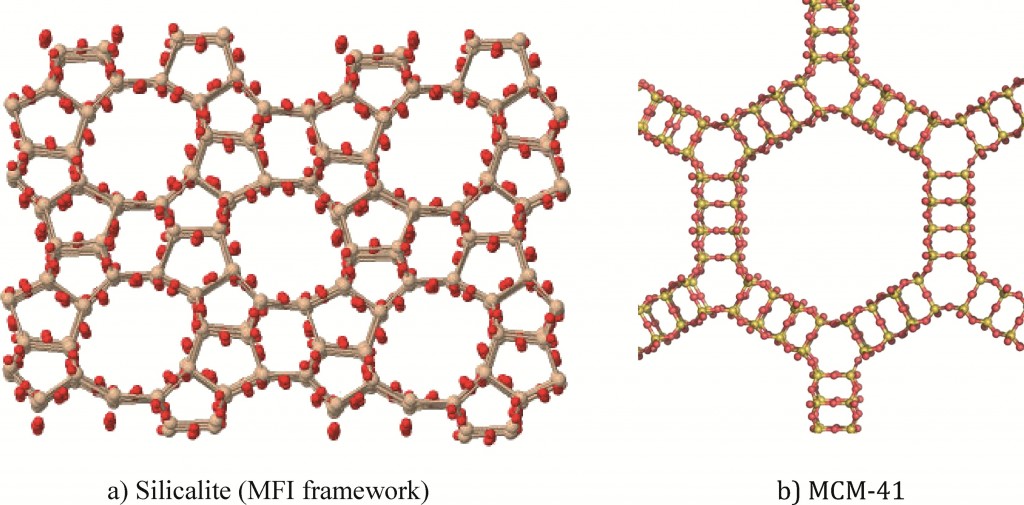
Zeolites and MSNs are silicate or aluminosilicate nanomaterials with well-defined pore networks; there are however some differences between the two porous nanomaterials.
Properties of zeolites:
- Crystalline aluminosilicates (or silicates)
- Regular arrangements of micropores
- High surface areas
- Exchangeable cations
Properties of MSN:
- Amorphous silica materials
- Regualr arrangement of mesopores
- Very high surface area
The first area discussed in this review is the synthesis of zeolite and MSNs using green synthetic routes. The green strategies can be organized into three main categories: solvent, template and heating. The diagram below demonstrates the strategies for the greener synthesis of zeolites and mesoporous silica.
*Access is free through a registered RSC account – click here to register